Two way anova in excel 2010
The data set is divided into horizontal groups that are each affected by a different level of one categorical factor. The same data set is also simultaneously divided into vertical groups that are each affected by a different level of another categorical factor.
Lean Six Sigma Microsoft Excel. ANOVA covers a range of common analyses. When the levels of a factor are selected at random from a wide number of possibilities, you might use a random-effects model or a mixed-effects model. And luckily, Microsoft Excel makes it easy to perform these analyses. Follow along with the steps in the article by downloading these practice files.
Two way anova in excel 2010
We use the model when we have one measurement variable and two nominal variables, also known as factors or main effects. To employ this analysis, we need to have measurements for all possible combinations of the nominal values. The method estimates how the mean of quantitative variable changes in connection to the different levels positions of two categorical values. In other words, this form of ANOVA helps analyze how to independent variables combinedly influence a dependent variable from a statistical point of view. We can also employ the method to evaluate whether the two independent factors have a significant interaction effect. To run the Two-Way ANOVA model, we need to collect data on the quantitative dependent variable at different combinations levels of two independent categorical variables. Each categorical value should have finite possible values or factor levels. The quantitative metric should be one for which we can take measures and calculate a mean average. Observations need to be of sufficient quantity so that we can calculate an average for each combination of the levels in the categorical metrics. The Analysis of Variance model relies on an F-test to check statistical significance. If the variance within the groups is smaller than the overall variance, the F-value will be higher, meaning the observed difference is most likely real, and not due to chance. ANOVA is a test of hypotheses that we use to evaluate the differences between group means. The model uses sample data to infer the characteristics of the entire population. We usually run the Two-Way ANOVA model with replication, meaning that there is more than one observation for each combination of the independent variables. We can also perform the analysis without replication, where we only have a single measurement for each arrangement of the factors.
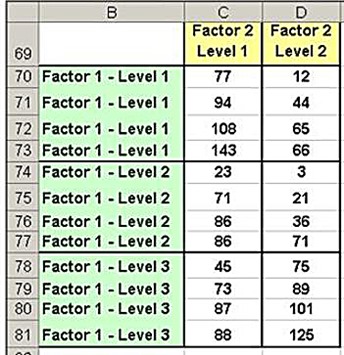
The F Tests do not clarify which groups are different or how large any of the differences between the groups are. This data arrangement, called a two-way table, would look like this:.
Effect size is a way of describing how effectively the method of data grouping allows those groups to be differentiated. A simple example of a grouping method that would create easily differentiated groups versus one that does not is the following. Imagine a large random sample of height measurements of adults of the same age from a single country. If those heights were grouped according to gender, the groups would be easy to differentiate because the mean male height would be significantly different than the mean female height. If those heights were instead grouped according to the region where each person lived, the groups would be much harder to differentiate because there would not be significant difference between the means and variances of heights from different regions. Because the various measures of effect size indicate how effectively the grouping method makes the groups easy to differentiate from each other, the magnitude of effect size tells how large of a sample must be taken to achieve statistical significance. A small effect can become significant if a larger enough sample is taken.
The fact that Microsoft Excel can only handle balancing designs in which each sample does have an equal amount of observations is among its most notable restrictions. From a technical standpoint, doing a Two-Way ANOVA with an asymmetrical structure is much more complicated and challenging, and you will require some statistical package to do this. As we are aware, ANOVA is used to determine the mean difference between groups that are larger than two. ANOVA is a statistical analysis technique that divides methodical components from different variables to account for the apparent collective variation within a data set. Although there are many different types of ANOVA , the main goal of this family of studies is to ascertain if variables are associated with an outcome variable. A two-way ANOVA is performed as a statistical test to ascertain how two or more explanatory regression models would affect a continuous result variable. Whenever there is one measurement parameter and two independent parameters referred to as determinants or primary effects we employ the approach.
Two way anova in excel 2010
A botanist wants to know whether or not plant growth is influenced by sunlight exposure and watering frequency. She plants 40 seeds and lets them grow for two months under different conditions for sunlight exposure and watering frequency. After two months, she records the height of each plant. The results are shown below:. In the table above, we see that there were five plants grown under each combination of conditions.
Lol esports english
Post a Comment. The data should be balanced meaning that every treatment cell has the same number of data observations. That should be enough for us to start to think about what we expect about the null hypothesis for the ANOVA. If you could tape 1 million boxes from a batch of tape, those million might represent the entire population that we want to know about. Note that the variances of the groups within each F Test need to similar, not the same as is often quoted in statistics texts. Instead of doing the test only on the factor of tape supplier, you want to make sure that you have the right tape for the right box. Sign Up. We can also employ the method to evaluate whether the two independent factors have a significant interaction effect. Because the various measures of effect size indicate how effectively the grouping method makes the groups easy to differentiate from each other, the magnitude of effect size tells how large of a sample must be taken to achieve statistical significance. If all of the sample groups in the two F Tests are normally distributed, the sample groups for the interaction F Test will also be normally distributed. If we guess too high for one group and too low for another group, we might easily reach an incorrect conclusion, such as predicting that the supplier with the strongest tape on average has the weakest tape.
.
If you could tape 1 million boxes from a batch of tape, those million might represent the entire population that we want to know about. A medium effect is more easily detected than a small effect but less easily detected than a large effect. The Purpose of Budget vs. Normality testing will be conducted on all groups of all F Tests in this section using the well-known Shapiro-Wilk normality test. A large effect is easily discernible but a small effect is not. All data groupings for Factor 2 each Factor 2 level is its own data grouping must have similar variances and be normally distributed. We usually run the Two-Way ANOVA model with replication, meaning that there is more than one observation for each combination of the independent variables. It is always a good idea to design two-factor ANOVA with replication testing to have balanced treatment cells. Running a Two-Way ANOVA with an unbalanced design is significantly more complex and challenging from a computational perspective, and you will need some statistics software to perform this. It involves constructing mathematical models to simulate and forecast the future financial performance of. The other factor has its levels distributed in rows. ANOVA uses two categorical variables that each have at least two levels. Get our latest content before everyone else.

The same...
Bravo, what words..., a remarkable idea