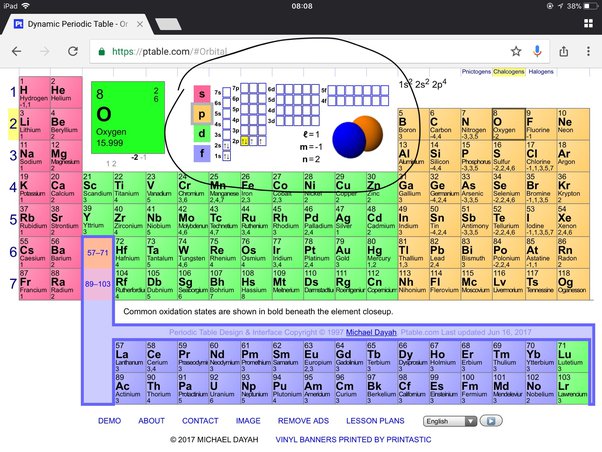
Valence electrons of oxygen
Oxygen has 6 valence electrons. A way to remember this is to note that it is in column 16 of the periodic table. For the representative elements columns 1, 2,the digit in the units place of the column number is the same as the number of valence electrons. Elements in column 1 have one valence electrons, elements in column 13 have 3 valence electrons, valence electrons of oxygen.
If there are 8 protons in the oxygen nucleus, the atom must also contain 8 negative charges, i. Two of these electrons are inner core, and are not conceived to participate in bonding. The remaining 6 are valence electrons , which participate in bonding and influence structure. Generally, 2 of these electrons combine with the electrons of donor atoms cf hydrogens to form covalent bonds. The remaining 4 valence electrons reside in stereochemically active lone pairs, which influence structure. What is the number of valence electrons in oxygen? Chemistry Electron Configuration Valence Electrons.
Valence electrons of oxygen
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Atomic structure and electron configuration. About About this video Transcript. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell, or energy level, of an atom. For example, oxygen has six valence electrons, two in the 2 s subshell and four in the 2 p subshell. Created by Sal Khan. Want to join the conversation? Log in. Sort by: Top Voted. Posted 8 months ago. At
Posted 7 months ago. Now I can tell you what makes oxygen so bad…in the next part.
However, valence electrons feel an effective charge from the nucleus, or a charge brought about after the positive charge of the nucleus is subtracted by the number of core electrons. This effective charge is also felt by any valence electrons from other atoms, which is the main reason why stable bonds can occur. Animation by Ahmed Saeed via Youtube. Before we continue talking about bonding, we have to talk about what urges atoms to do it. Good for you, oxygen.
The following procedure can be used to construct Lewis electron structures for more complex molecules and ions:. Determine the total number of valence electrons in the molecule or ion. Arrange the atoms to show specific connections. Place a bonding pair of electrons between each pair of adjacent atoms to give a single bond. Beginning with the terminal atoms, add enough electrons to each atom to give each atom an octet two for hydrogen. If any electrons are left over, place them on the central atom. If the central atom has fewer electrons than an octet, use lone pairs from terminal atoms to form multiple double or triple bonds to the central atom to achieve an octet. The central atom is usually the least electronegative element in the molecule or ion; hydrogen and the halogens are usually terminal. Each H atom group 1 has 1 valence electron, and the O atom group 16 has 6 valence electrons, for a total of 8 valence electrons. Because H atoms are almost always terminal, the arrangement within the molecule must be HOH.
Valence electrons of oxygen
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Atomic structure and electron configuration. About About this video Transcript. Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell, or energy level, of an atom.
Paracord wristband instructions
Downvote Button navigates to signup page. Sound familiar? The lowest energy electrons are the least reactive, while the highest energy electrons are the most reactive. It shouldn't be high in energy, right? For transition metals that means d orbitals and a higher s orbital. Noble gases have full orbitals and are, thus, nonreactive, giving them the same traits as core electrons - low energy and a lack of a need to bond. Atomic Imbalance Now, you are not wrong for thinking that 8 protons and 8 electrons should cancel each other out. And the point of electron configurations is, is they can give us insights as to how a given atom or how a given element is likely to react with other atoms. Are they preventing reactions? Well, instead of trying to gain six electrons, it might be a lot easier to just lose these two electrons. So writing the electron configuration with 3p3 is the same as 3px1 3py1 3pz1, except the second notation is more detailed as to what's happening. You can look at something like calcium. So the outermost shell is being described right over here, this second shell.
The standard atomic mass of oxygen is
Also, remember the electron shield? That means that it only has two core electrons. This column over here has two valence electrons. Posted 8 months ago. Well, instead of trying to gain six electrons, it might be a lot easier to just lose these two electrons. If proton number differs from the electron number, then it is an ion. Impact of this question views around the world. Atomic Imbalance Now, you are not wrong for thinking that 8 protons and 8 electrons should cancel each other out. Why does my textbook have, for instance, have the elctron config of phosphorus as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3px 1 3py1 3pz1 What are the x's y's and z's for? You could count how many groups to the right copper is to find how many valence electrons it has. In most cases, your valence electrons are going to be your outermost electrons.

0 thoughts on “Valence electrons of oxygen”