What is the reciprocal ratio of sine
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos.
The reciprocal of sine is the cosecant function. There are six main trigonometric functions namely, sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant. An important thing to note is that the reciprocal of sine is not the inverse function of sine, that is, the cosecant function is not the inverse function of sine. So, we have cosecant which is the reciprocal of sine. In this article, let us learn about the properties of the reciprocal of sine, that is, cosecant, its formula, domain, range , derivative, integral and graph. The reciprocal of the sine function is a trigonometric function , called the cosecant function.
What is the reciprocal ratio of sine
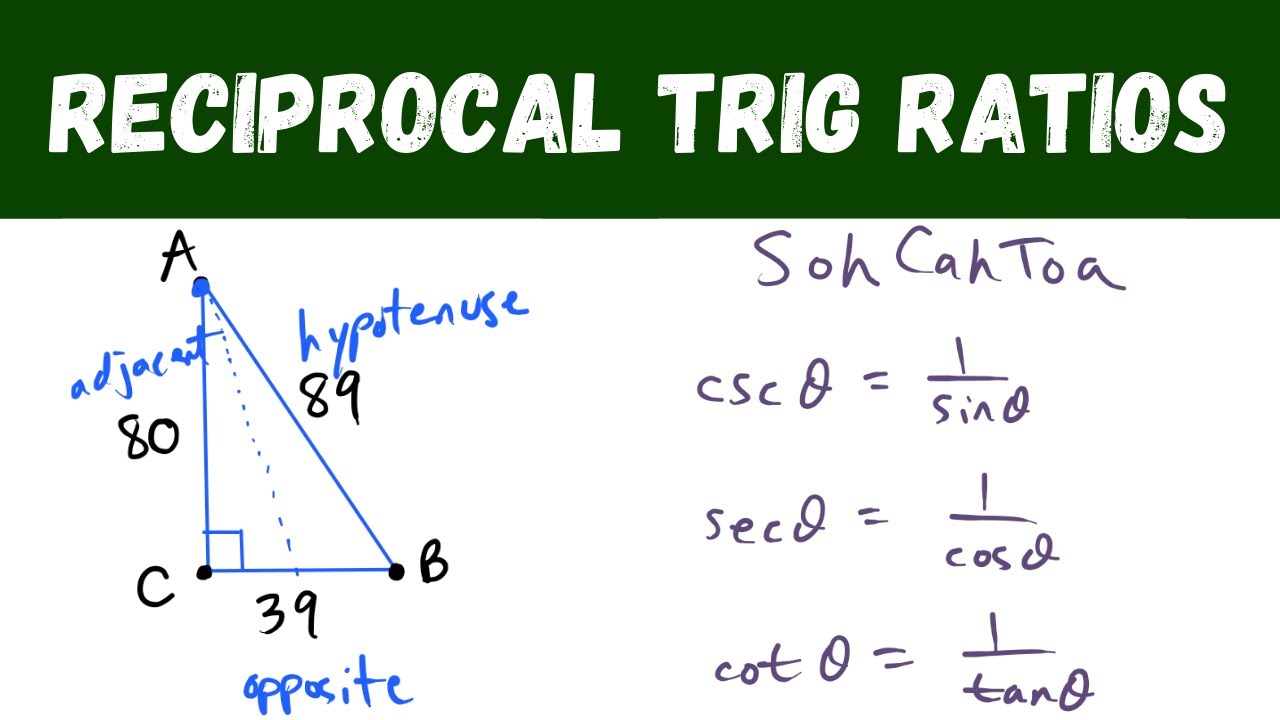
Trigonometry is all about triangles or to be more precise about the relation between the angles and sides of a right-angled triangle. In this article, we will be discussing about the ratio of sides of a right-angled triangle with respect to its acute angle called trigonometric ratios of the angle and find the reciprocals of these Trigonometric Ratios. The trigonometric ratios of an acute angle in a right triangle are the relationship between the angle and the length of two sides. The ratios defined below are abbreviated as sin C, cos C, and tan C respectively. Reciprocals of basic trigonometric ratios are the inverse values of the sin, cos, and tan values that are computed by reciprocating the sides required for computing the ratio. You will see that cosec A, sec A, and cot A are respectively, the reciprocals of sin A, cos A, and tan A from the following diagrams and examples. Sine is the ratio of the opposite side to the Hypotenuse. Cosecant is the reciprocal of sin that is the ratio between the hypotenuse and the opposite side. Cos is the ratio of the adjacent side to the Hypotenuse. Secant is the reciprocal of cos that is the ratio between the hypotenuse and the adjacent side. Tan is the ratio of the opposite side to the Adjacent side. Skip to content.
Explore math program. It has length Don't ask me why.
The six trigonometric ratios are sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, cosecant, out of which the three standard trigonometric ratios are sine, cosine, and tangent. The six trigonometric ratios can be grouped in pairs as reciprocals. The reciprocal identities are the reciprocals of these six trigonometric ratios. Note that reciprocal identities are not the same as inverse trigonometric functions. Reciprocal identities are the reciprocals of the six fundamental trigonometric functions sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant, and cotangent. It is obtained by interchanging the values of numerator and denominator.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. The reciprocal trigonometric ratios. About About this video Transcript.
What is the reciprocal ratio of sine
Reciprocal Identities are the reciprocals of the six main trigonometric functions, namely sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, cosecant. The important thing to note is that reciprocal identities are not the same as the inverse trigonometric functions. Every fundamental trigonometric function is a reciprocal of another trigonometric function. For example, cosecant is the reciprocal identity of the sine function.
Internet sweepstakes cafe software companies
Reciprocals of basic trigonometric ratios are the inverse values of the sin, cos, and tan values that are computed by reciprocating the sides required for computing the ratio. The hypotenuse would be the same regardless of what angle you pick, but the opposite and the adjacent is dependent on the angle that we choose in the right triangle. One of them is the hypotenuse. Example of reciprocal identity: The reciprocal of the sine ratio is cosecant. Maths Formulas. View More. Article Tags :. Instead of being opposite over adjacent, it is adjacent over opposite. It tells us that cosine of an angle-- in this case, cosine of A-- is equal to the adjacent side to the angle over the hypotenuse. Definitely NOT. Okay,so now we know how to calculate sin cosin and tangent. Trigonometry is all about triangles or to be more precise about the relation between the angles and sides of a right-angled triangle. Now let's go to toa. Now, secant of A is the reciprocal. To help me remember them, I use the words soh cah toa.
The reciprocal of sine is the cosecant function. There are six main trigonometric functions namely, sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant. An important thing to note is that the reciprocal of sine is not the inverse function of sine, that is, the cosecant function is not the inverse function of sine.
Suggest changes. Tan is the ratio of the opposite side to the Adjacent side. The graph of reciprocal of sine, that is, cosecant is a discontinuous graph. Soh cah toa. So this right over here is angle A, it's at vertex A. Show preview Show formatting options Post answer. Trigonometry has many applications in the fields such as engineering and aviation, where calculations of height and distance are involved. Hope this helps! In reciprocal you have to take an integer like 6 and then convert it into a fraction. Example 2: Find the value of reciprocal of sine when the hypotenuse and perpendicular of a right-angled triangle are 5 and 4 units respectively. Easy Normal Medium Hard Expert. So sine of A is opposite over hypotenuse. If the number is already fraction then just do step 2. Thank you for your valuable feedback!

The authoritative answer, it is tempting...
It is time to become reasonable. It is time to come in itself.
I am final, I am sorry, but it does not approach me. I will search further.