What muscles do the plank work
Exhibit one: the plank, what muscles do the plank work. In its most basic form, the plank is exceedingly straightforward—just assume a pushup position with your arms straight or forearms on the floor and hold that posture for the prescribed amount of time or for as long as you can before failure. But despite its simplicity, the plank can help you build core strength more quickly than most other abdominal exercises—especially those that involve movement, like the crunch—according to a study in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research.
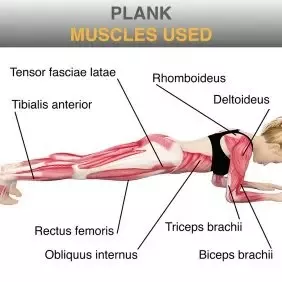
Planks can help work your core muscles, as well as your upper and lower body. There are different types of planks that may have slightly different benefits. The plank is a full body exercise, meaning it targets muscles of the upper body, core, and lower body. In particular, your rectus abdominis , obliques, and transverse abdominis are utilized 1 , 2 , 3. The rectus abdominis is the top layer of muscles of your stomach. It helps cinch your waist and stabilize your back muscles 4 , 5.
What muscles do the plank work
The plank is a fantastic way to build core strength and endurance. In this guide, we dive into detail about all things plank. The plank mainly works four muscle groups, your rectus abdominus, transverse abdominus, internal obliques and external obliques. Typically, these muscles are used to flex the spine e. Your Transverse Abdominus: Your transverse abdominus are your deeper core muscles responsible for stabilisation of your torso, as well as maintaining good daily posture. Your transverse abdominus works in the plank to hold you stable and braced. Your Internal Obliques: Located more towards the side of your abdomen, your internal obliques assist with hip and back stability during the plank, keeping your body level. Your External Obliques: Your external obliques are located a layer above your internal obliques. During a plank, they work to provide hip and back stability, as well as helping to resist spine extension. What about traps, rhomboids, biceps, triceps etc? This is technically true, but to such a minor extent that it barely counts. Getting the core strength, stability and endurance benefits of the plank requires good execution of the movement. The plank on knees still works the rectus abdominus, transverse abdominus, internal and external obliques. The main difference is that it works these muscles with less intensity. The straight arm plank is a plank variation in which you use straight arms and place your weight on your hands rather than your forearms.
Just make sure you can hold with perfect form, and let that dictate how long you hold. In This Article View All.
Ah, planks. But anyone who's ever taken a group fitness class knows that they are a deceptively difficult exercise. A plank is an isometric exercise that involves getting into a push-up position, and then staying put, explains physical therapist Grayson Wickham , D. Yes, this equipment-free move works your core, upper body, and lower body. The best part? The plank is a safe and effective exercise for people of all fitness levels.
Planks are a great way to build up your core strength. But in addition to your abs, planks activate many other muscles throughout the body. You'll also work your back, butt, legs, and shoulders as you hold a plank. There are three types of planks that each target different muscles: beginner, intermediate-to-advanced, and side plank variations. You'll also use your back muscles to keep the plank position. Your core muscles are the center of your body, and they help you move in every direction.
What muscles do the plank work
The plank is a fantastic way to build core strength and endurance. In this guide, we dive into detail about all things plank. The plank mainly works four muscle groups, your rectus abdominus, transverse abdominus, internal obliques and external obliques. Typically, these muscles are used to flex the spine e. Your Transverse Abdominus: Your transverse abdominus are your deeper core muscles responsible for stabilisation of your torso, as well as maintaining good daily posture. Your transverse abdominus works in the plank to hold you stable and braced. Your Internal Obliques: Located more towards the side of your abdomen, your internal obliques assist with hip and back stability during the plank, keeping your body level. Your External Obliques: Your external obliques are located a layer above your internal obliques. During a plank, they work to provide hip and back stability, as well as helping to resist spine extension. What about traps, rhomboids, biceps, triceps etc?
Ups customer service jobs
The straight arm plank is a plank variation in which you use straight arms and place your weight on your hands rather than your forearms. Trevor Thieme C. There is only constant contraction on a head-to-toe scale that must be held until you can hold it no more. A common mistake, but your body should be flat as opposed to an upside down-V shape. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19 5 , There are many aesthetic dividends to adding the plank to your training program, including a flatter stomach, leaner profile, and more defined abs. Be sure to only perform advanced planks when you can safely perform a standard plank. For a modified plank, Blades suggests dropping to your knees instead of holding yourself up on your toes. If, however, you are a seasoned pro he suggests adding them to the end of your workout. Your External Obliques: Your external obliques are located a layer above your internal obliques. Variations of the plank exercise. If you just move your arms or leg on their own, it works these muscles less, if you move your arms and legs at the same time, the deadbug works these muscles much more. Use profiles to select personalised content. A plank is an isometric exercise that involves getting into a push-up position, and then staying put, explains physical therapist Grayson Wickham , D.
Ah, planks.
Measure advertising performance. Axler, C. The plank is a fantastic way to build core strength and endurance. Screw pinkies into the ground and away from the body to activate lats. The Benefits of Planks There are many aesthetic dividends to adding the plank to your training program, including a flatter stomach, leaner profile, and more defined abs. In This Article View All. Due to the angle, some people find it a little easier, whilst others find it harder on their shoulders and wrists. From bending for grocery bags to swinging a golf club, your core plays a key role. When the obliques on both sides of your body work in tandem, they also provide a stabilizing effect, particularly by holding the ribs and hips in alignment 1 , 2 , 3. Increasing stability in the lumbar spine may help reduce and prevent lower back pain 9 , 10 , Use profiles to select personalised content. You can then add more sets and build up your training that way. For instance, you could put your toes on a tree and do a decline plank, or you could put your hands on a park bench and do an incline plank. Trevor Thieme C.

You are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM.
Bravo, you were visited with simply excellent idea