What replaced the encomienda system
The encomienda system was a labor system instituted by the Spanish crown in the American colonies. In this system, a Spanish what replaced the encomienda system was granted a number of native laborers who would pay tributes to him in exchange for his protection, what replaced the encomienda system. In the early 16th century, the Spanish crown set up the encomienda system in the Americas to divide up the American Indian walmart tiedeman force in order to aid the development of their mining ecomony. Under this system a Spanish conquistador, or another prominent male Spaniard known as an encomenderowas granted the labor of a certain number of Native Americans living in the area.
The labourers, in theory, were provided with benefits by the conquerors for whom they laboured, including military protection and education. The encomienda was first established in Spain following the Christian reconquest of Moorish territories known to Christians as the Reconquista , and it was applied on a much larger scale during the Spanish colonization of the Americas and the Spanish East Indies. Conquered peoples were considered vassals of the Spanish monarch. The Crown awarded an encomienda as a grant to a particular individual. In the conquest era of the early sixteenth century, the grants were considered to be a monopoly on the labour of particular groups of indigenous peoples , held in perpetuity by the grant holder, called the encomendero ; starting from the New Laws of , the encomienda ended upon the death of the encomendero , and was replaced by the repartimiento. Encomiendas devolved from their original Iberian form into a form of "communal" slavery.
What replaced the encomienda system
During the 16 th century, Spanish imperialists employed the encomienda system during their conquest of the Americas and the Philippines. Although in name indigenous people were assigned to be in charge of the labor, the natives were vastly mistreated. This setup led to decades of enslavement and exploitation of Native American peoples and perpetuated the cruel domination by the Spanish in the New World. Since its establishment in , the encomienda system was under scrutiny. He pushed for the New Laws in , which gave indigenous peoples certain rights and allowed for the gradual abolition of the encomienda system. However, these laws were met with revolts from the encomenderos who were in charge of plots of land with slave labor. Ultimately the encomienda system continued until The Spanish took advantage of the rich resources in the New World, especially gold, silver, corn, indigo, and sugar cane. In order to make use of these resources and still make a profit, the Spaniards instituted a system of slavery so they would have a constant supply of free labor in their colonies. The Spanish often divided up communities and families in the Caribbean to fit their own labor needs. Eventually , the encomienda system was replaced by repartimiento , in which the native workers were allotted directly to the Spanish monarchy rather than individual Spaniards in the colonies. The natives were then assigned to settlers for a certain amount of time, usually only for a few weeks. This system was intended to reduce the amount of abuse of the workers.
In addition, the encomienda system had a large impact on the what replaced the encomienda system of intermarriage between races in the New World. Later, some receiving encomiendas in New Spain Mexico were not conquerors themselves but were sufficiently well connected that they received grants. The attempt failed, as encomenderos ignored the laws and revolted against any attempt to weaken their power of the their laborers.
.
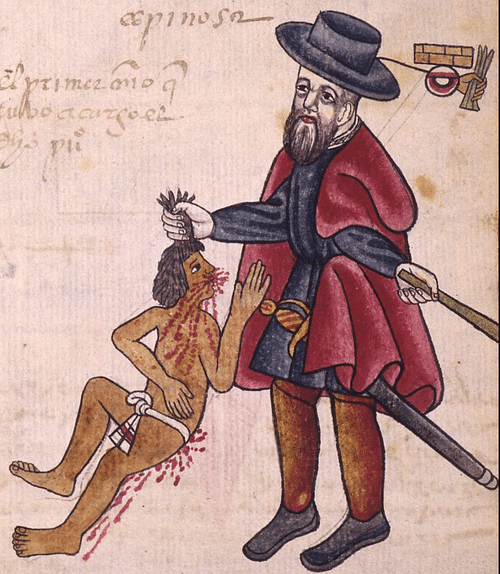
With Indigenous governments such as the efficient Inca Empire in ruins, the Spanish conquistadors needed to find a way to rule their new subjects. The encomienda system was put in place in several areas, most importantly in Peru. Under the encomienda system, prominent Spaniards were entrusted with Native Peruvian communities. In exchange for the stolen labor of Indigenous people and tribute, the Spanish lord would provide protection and education. In reality, however, the encomienda system was thinly-masked enslavement and led to some of the worst horrors of the colonial era. The word encomienda comes from the Spanish word encomendar , meaning "to entrust. In the Americas, the first encomiendas were handed out by Christopher Columbus in the Caribbean. Spanish conquistadors, settlers, priests, or colonial officials were given a repartimiento , or grant of land. These lands were often quite vast. The land included any Indigenous cities, towns, communities, or families that lived there.
What replaced the encomienda system
During the s, Spain expanded its colonial empire to the Philippines in the Far East and to areas in the Americas that later became the United States. The Spanish dreamed of mountains of gold and silver and imagined converting thousands of eager Native Americans to Catholicism. In their vision of colonial society, everyone would know his or her place. Patriarchy the rule of men over family, society, and government shaped the Spanish colonial world. Women occupied a lower status. In all matters, the Spanish held themselves to be atop the social pyramid, with Native peoples and Africans beneath them. Both Africans and native peoples, however, contested Spanish claims to dominance.
Shadow of war bow
Encomiendas have often been characterized by the geographical displacement of the enslaved and breakup of communities and family units, but in New Spain , the encomienda ruled the free vassals of the crown through existing community hierarchies, and the natives remained in their settlements with their families. In addition, the encomienda system had a large impact on the tradition of intermarriage between races in the New World. Here is an example question similar to one that might appear on the exam:. University of Minnesota Press. Yale University. Terra Australis. ISBN August 21, Eventually, the encomienda system was replaced by the repartimiento system, but it was not abolished until the late 18th century. Hi Stuart, Thank you for bringing this to our attention! The encomienda was first established in Spain following the Christian reconquest of Moorish territories known to Christians as the Reconquista , and it was applied on a much larger scale during the Spanish colonization of the Americas and the Spanish East Indies. This differs from the written section, which will ask you to make comparisons and connections across US history and among different movements and concepts. August 28, Core Subject Review Guides. Kindle Edition.
The encomienda system played a major role in helping Spain expand its colonies in the New World.
The system was intended to be a way to enter into a peaceable and mutually beneficial relationship with the indigenous peoples of America; however, the system quickly devolved into essentially a system of slavery. They benefited from the discovery of gold and silver in the New World, and the mining of those metals by their laborers. The system of encomiendas was aided by the crown's organizing the indigenous into small harbors known as reducciones , with the intent of establishing new towns and populations. The Encomienda System was ended legally in Christophere SanJuan. Main article: New Laws. Columbus and Las Casas: the conquest and Christianization of America, — Later, a chieftain named Guarionex laid havoc to the countryside before an army of about 3, routed the Ciguana people under his leadership. The encomienda system granted a Spanish leader a number of Native American laborers. The encomenderos were then required to pay remaining encomienda labourers for their work. Interested in a school license? Hi there! By country or region. Spain began the encomienda system in the New World at the beginning of the 16th century. University Press of America.

In my opinion, it is a lie.
I understand this question. I invite to discussion.
The good result will turn out