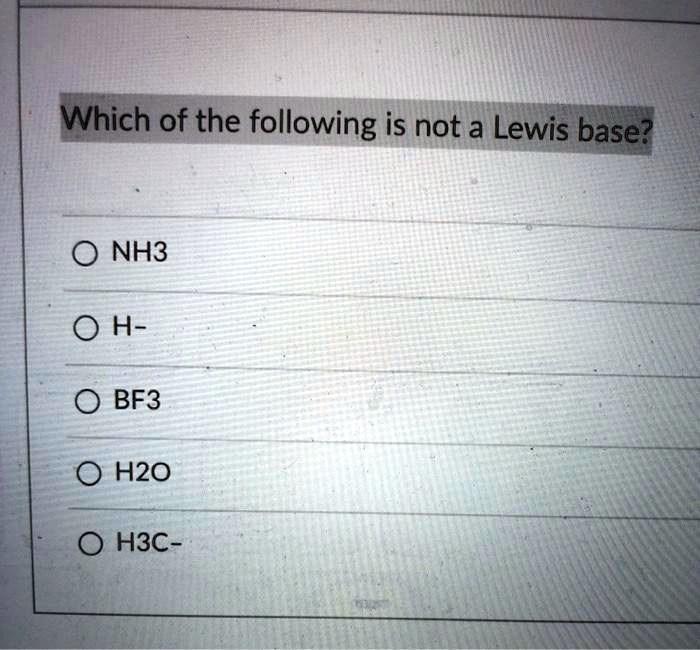
Which of the following is a lewis base
In G. In the Lewis theory of acid-base reactions, bases donate pairs of electrons and acids accept pairs of electrons.
The Lewis concept of acidity and basicity will be of great use to you when you study reaction mechanisms. The realization that an ion such as. A broader definition is provided by the Lewis theory of acids and bases, in which a Lewis acid is an electron-pair acceptor and a Lewis base is an electron-pair donor. The carbonyl oxygen the Lewis base donates a pair of electrons to the magnesium cation the Lewis acid. As we will see in chapter 11 when we begin the study of reactions involving carbonyl groups, this interaction has the very important effect of increasing the polarity of the carbon-oxygen double bond. This, too, has the effect of increasing the polarity of the carbonyl double bond. Borane is unusual because it is a compound without an octet.
Which of the following is a lewis base
What makes a molecule or an atom or ion a Lewis base? It must have a pair of electrons available to share with another atom to form a bond. The most readily available electrons are those that are not already in bonds. Bonding electrons are low in energy. Non-bonding electrons are higher in energy and may be stabilized when they are delocalized in a new bond. Ammonia, NH 3 , has a lone pair and is a Lewis base. It can donate to compounds that will accept electrons. Lewis bases may be anionic or neutral. The basic requirement is that they have a pair of electrons to donate. Examples of Lewis bases include halide ions such as bromide or chloride. To the right of the halides in the periodic table are Noble gases such as neon.
One column further to the left in the periodic table from nitrogen is carbon.
.
Lewis acids and bases are described by the Lewis theory of acid-base reactions as electron-pair acceptors and electron pair donors respectively. Therefore, a Lewis base can donate a pair of electrons to a Lewis acid to form a product containing a coordinate covalent bond. This product is also referred to as a Lewis adduct. An illustration detailing the reaction between a Lewis acid and base leading to the formation of a coordinate covalent bond between them is given below. Lewis acids and bases are named after the American chemist Gilbert Newton Lewis, who also made invaluable contributions in the fields of thermodynamics and photochemistry.
Which of the following is a lewis base
Make sure you thoroughly understand the following essential ideas which have been presented. It is especially important that you know the precise meanings of all the highlighted terms in the context of this topic. But as with any such theory, it is fair to ask if this is not just a special case of a more general theory that could encompass an even broader range of chemical science.
Bob with choppy bangs
The Lewis concept of acidity and basicity will be of great use to you when you study reaction mechanisms. Search for:. As a result, the boron atom is sp 2 hybridized, which leaves an empty 2 p z orbital on the boron atom. It can donate to compounds that will accept electrons. Another term for this kind of bond is a dative bond. In other words, a Lewis acid is an electron-pair acceptor. Problem Which of the following compounds appear to be Lewis bases? Note that neon, although it has nonbonding electron pairs or lone pairs, does not usually act as a Lewis base. Figure 2: Boron, aluminum and indium are from the same column of the periodic table. Donation of electrons from a Lewis base to a Lewis acid. Lewis bases may be anionic or neutral. As a result, hydrogen often has a partial positive charge. These bonding pairs are too stable to donate under normal conditions. Lewis bases may be anionic or neutral.
A Lewis acid named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N.
Many of the other elements commonly found in compounds with hydrogen are more electronegative than hydrogen. In the main group of the periodic table, atoms in the Group 13 column including boron and aluminum have three valence electrons to share in order to make bonds. The boron has no octet and is an electron acceptor. Figure 5: A few alkali, alkaline earth and transition metals that are commonly found as cations. It is the hydrogen cation or proton. Examples of Lewis bases include halide ions such as bromide or chloride. Non-bonding electrons are higher in energy and may be stabilized when they are delocalized in a new bond. It can donate to compounds that will accept electrons. Ammonia, NH 3 , has a lone pair and is a Lewis base. When a neutral Lewis acid combines with an anionic Lewis base, the product is called a complex ion.

There is nothing to tell - keep silent not to litter a theme.
I am sorry, that has interfered... This situation is familiar To me. Is ready to help.