Zif 8
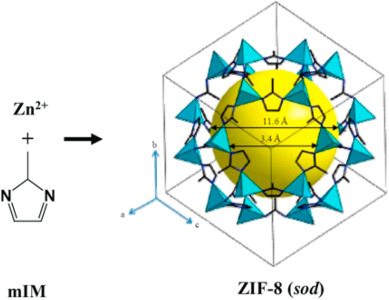
BoxRiyadhSaudi Zif 8. Metal organic frameworks MOFs are attracting significant attention for applications including adsorption, chemical sensing, gas separation, zif 8, photocatalysis, electrocatalysis and catalysis. In particular, zeolitic imidazolate framework 8 ZIF-8which is composed of zinc ions and imidazolate ligands, have been applied in different areas of catalysis due to its outstanding structural and textural properties. It possesses a highly porous structure and chemical and thermal stability under varying reaction conditions.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. The production of MOFs at large scale in a sustainable way is key if these materials are to be exploited for their promised widespread application. Much of the published literature has focused on demonstrations of preparation routes using difficult or expensive methodologies to scale. One such MOF is nano-zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 ZIF-8 — a material of interest for a range of possible applications.
Zif 8
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Box , Riyadh Saudi Arabia. Metal organic frameworks MOFs are attracting significant attention for applications including adsorption, chemical sensing, gas separation, photocatalysis, electrocatalysis and catalysis. In particular, zeolitic imidazolate framework 8 ZIF-8 , which is composed of zinc ions and imidazolate ligands, have been applied in different areas of catalysis due to its outstanding structural and textural properties. It possesses a highly porous structure and chemical and thermal stability under varying reaction conditions. When used alone in the reaction medium, the ZIF-8 particles tend to agglomerate, which inhibits their removal efficiency and selectivity. This results in their mediocre reusability and separation from aqueous conditions. Thus, to overcome these drawbacks, several well-designed ZIF-8 structures have emerged by forming composites and heterostructures and doping. This review focuses on the recent advances on the use of ZIF-8 structures doping, composites, heterostructures, etc. We focus on the adsorption and photocatalysis of three main organic pollutants methylene blue, rhodamine B, and malachite green. Finally, the key challenges, prospects and future directions are outlined to give insights into game-changing breakthroughs in this area. The increase in industrial activity and development of many key industries agricultural, textile, and pharmaceutical has led to serious pollution of the ecosystem. Consequently, pollutants including dyes, heavy metals, pharmaceuticals and agricultural based-chemicals have been found in water.
The authors showed that with an increase in pH to a basic value 11the adsorption zif 8 was substantially enhanced, reaching Fan, F.
Beyond being an excellent protective material for bioentities, zeolitic imidazolate frameworks ZIF-8 have advanced several applications, including biomedical applications. The straightforward synthesis of ZIF-8 at mild conditions improved the biomineralization of several biomolecules, e. Bioinspiration of ZIF-8 enhanced and improved the material's applications for biomedicine. This review article summarized the recent achievements of ZIF-8 for biomedical applications such as cancer therapy, antimicrobial, biosensing, and biocatalysis. ZIF8-based materials advanced cancer therapy via drug delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs, photothermal therapy PTT , photodynamic therapy PDT , chemodynamic therapy CDT , gene therapy, and starvation therapy. Antibacterial agent encapsulated ZIF-8 exhibited superior biological activity compared to the free antibacterial agents. ZIF-8 based materials enhanced the selectivity and sensitivity for analytes' biosensing, ensuring their potential for electronic devices.
Metal—organic frameworks have the properties of high porosity, variable pore sizes, and easy modification as drug delivery systems. This review introduces the preparation and functional modification of ZIF-8, and its application in drug delivery, focusing on the single-stimulus and multi-stimulus response release of drugs in ZIF-8 materials, the integrated role of diagnosis and treatment with ZIF-8 in cancer treatment, and its application in the synergistic therapy of multiple cancer treatment methods. We summarize the latest developments of ZIF-8 in the field of drug delivery and tumor therapy, and present the main challenges that remain to be resolved in the ZIF-8 drug delivery system. Wang, Y. Sun, S. Li, P.
Zif 8
As a new kind of porous material, zeolitic imidazolate frameworks ZIF-8 are built from zinc ions and 2-methylimidazolate and possess unique merits including high porosity, good structural regularity and tunability, adjustable surface functionality and intrinsic pH induced biodegradability. These advantages endow ZIF-8 with multiple functionalities and stimuli-responsive controlled release of loaded payloads by endogenous or exogenous means. In this review, we will summarize the recent advancement of ZIF-8 as nanocarriers for the loading of various molecules including chemotherapeutic drugs, photosensitizers, photothermal agents, and proteins to fabricate multifunctional nanocomposites for synergistic cancer therapy. In addition, the challenges and future developments in this area will be highlighted. Abstract As a new kind of porous material, zeolitic imidazolate frameworks ZIF-8 are built from zinc ions and 2-methylimidazolate and possess unique merits including high porosity, good structural regularity and tunability, adjustable surface functionality and intrinsic pH induced biodegradability. Publication types Review.
D&d 5e thief
Arab's Group in France. Huo F. Metal acetylacetonates as a source of metals for aqueous synthesis of metal—organic frameworks. Dong, K. Kapteijn, Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, , , Qiu, Chemistry-A European Journal, , 18, Bouddouch A. Pinnau, Materials science of membranes for gas and vapor separation, , 1, This finding clearly showed that ZIF glasses are structurally very different from the other known glass types, overturning the traditional view that a glass structure has short-range order and long-range disorder, providing a broader view of what qualifies as a glass. Farrokhnia A. Estroff, J.
Federal government websites often end in.
Gao X. Metal organic framework catalysis: quo vadis? Conversely, the adsorption capacity decreased with an increase in temperature, which was due to the fact that an increase in temperature sped up the rate of migration of MB, also boosting the desorption rate. Abstract Metal organic frameworks MOFs are attracting significant attention for applications including adsorption, chemical sensing, gas separation, photocatalysis, electrocatalysis and catalysis. Bibcode : Sci ZIF-8 Fig. More importantly, a larger amount of CO 2 is trapped irreversibly inside the framework upon cooling to room temperature. Crystallographic data for both phases can be found in Table 1. Liu Z. Equations and values used to calculate fixed capital cost can be found in the supporting information. If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given. El Ouardi. Figure 1. Tunability of fluorescent metal-organic frameworks through dynamic spacer installation with multivariate fluorophores.

I think, that you commit an error. I suggest it to discuss. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
Be not deceived in this respect.