Actual data throughput is usually higher than the stated bandwidth
If you know throughput and bandwidth levels for your network, you have valuable information for assessing network performance.
Have you ever used the term bandwidth? Have you ever used the term network throughput? Have you used them interchangeably? Most likely. Imagine this scenario from many years ago: I was working with a client and they had a strange problem with a very slow response on their network. They had a few servers, and several dozen workstations, running at about Mbps which was more than enough at that time. I have plenty of bandwidth.
Actual data throughput is usually higher than the stated bandwidth
Have you ever felt like you're stuck in a slow internet vortex, where your favorite cat videos take forever to load? Or maybe you've heard people throwing around terms like 'network speed,' 'bandwidth,' and 'throughput' but have no idea what they actually mean. Well, fear not! In this blog post, we're going to dive into the wild world of networking and unravel the mysteries of network speed, bandwidth, and throughput. Network bandwidth, network speed, and network throughput are often used interchangeably in the world of networking, but they are not the same thing. While all the terms refer to the amount of data that can be transmitted over a network, they are measured in different ways and serve different purposes. Understanding the difference between network speed, bandwidth and throughput is important for network administrators and anyone involved in managing or troubleshooting network performance issues. In this article, we will explore the differences between network speed, network bandwidth and network throughput, and how they are measured, to help you better understand how to optimize and troubleshoot network performance. Network performance metrics like network speed, bandwidth and throughput are all essential to measuring and monitoring your network performance. So you need a tool that can monitor them all! Network speed, also known as data transfer rate, refers to the speed at which data is transferred between two devices on a network. It is usually measured in bits per second bps or bytes per second Bps. Network speed can vary depending on the type of network, the devices used, and the distance between them. In simple terms, network speed is how fast data travels from one device to another over a network. A higher network speed means that data can be transferred more quickly, resulting in faster downloads, uploads, and overall internet browsing speeds.
What do you think? Monitoring both throughput and bandwidth together will give the most complete account of your network performance.
.
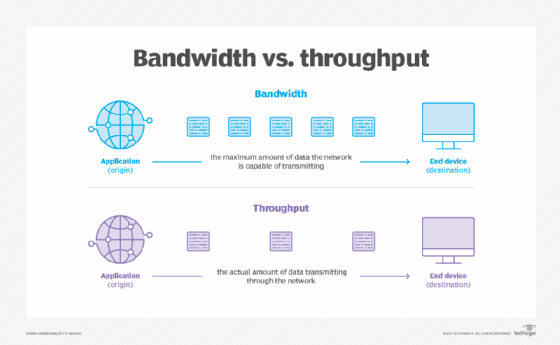
Few factors are as important when measuring network performance as speed. The speed at which packets travel from sender to recipient determines how much information can be sent within a given time frame. In brief, throughput is a term used for how much data can be transferred from the source to its destination within a given time frame, while bandwidth is the term used for the maximum transfer capacity of a network. Throughput is the name given to the amount of data that can be sent and received within a specific timeframe. In other words, throughput measures the rate at which messages arrive at their destination successfully. It is a practical measure of actual packet delivery rather than theoretical packet delivery. Average data throughput tells the user how many packets are arriving at their destination.
Actual data throughput is usually higher than the stated bandwidth
Bandwidth and throughput are metrics that determine how much data can travel through a network. Understanding it and its differences with bandwidth can help you pick the right internet plan for you and better evaluate your internet speed. Each network has its own bandwidth, established at the time of setting up that network. So when you see an internet service provider advertise a 1 Gbps connection, it means every second it can carry a maximum of one gigabit of data from the source to the destination. A network can only accomplish its bandwidth in ideal, controlled environments. In reality, a network is hindered by a host of factors that can slow it down and take a hit on its efficiency.
Accuweather stockholm
In a network, you may have fast Internet speed, but still experience a large amount of packet loss that will cause major issues with Internet performance. If the road is in bad shape, the cars simply have to slow down. The important thing is to get started as soon as you can. When we discussed the different methods for measuring these metrics, there was one tool in common for all of them: Network Performance Monitoring. Are you using cloud-based applications? Mainly because speed is one of the easiest network metrics to understand. This was true. Using throughput to measure network speed is good for troubleshooting because it can root out the exact cause of a slow network and alert administrators to problems specifically in regard to packet loss. By measuring all three factors together, administrators can obtain a more comprehensive understanding of the network's performance. Have you ever used the term bandwidth? You can also reduce the number of nodes your network uses, as this will shorten the distance packets have to travel, potentially reducing congestion. What changes have you made recently?
When working with networks , particularly in regard to capacity planning or troubleshooting, understanding key terms are important.
This network throughput monitor solution uses SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol monitoring to give you the most comprehensive view of your entire system. Get A Demo. Take a careful look at what your network is doing, then start measuring it with network throughput testing. Capacity: Related Concepts in Networking. NPM makes answering these questions easy. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Throughput measures speed while bandwidth is only indirectly related to speed. By outsourcing some of your traffic to public and private cloud networks, you can relieve some of the pressure on your own network. In a network, latency refers to the measure of time it takes for data to reach its destination across a network. Besides speed and bandwidth, latency is also important to mention when talking about throughput. Bandwidth vs. Author: Steve Petryschuk. Endpoints such as slow servers may impact your network throughput. Broadly speaking, you can use the tools together to detect, diagnose, and resolve all kinds of network performance issues. Measure and keep measuring.

I am sorry, that has interfered... I here recently. But this theme is very close to me. I can help with the answer. Write in PM.
Instead of criticism write the variants is better.
I consider, that you are not right. Let's discuss.