Approx atomic mass of first 30 elements
The atomic mass of elements is measured with the help of unified atomic mass units, approx atomic mass of first 30 elements. One unified atomic mass unit can be quantified as the weight of one-twelfth of the mass of a carbon atom considering that it is at rest. Since protons and neutrons account for almost all of the mass of the given atom, the atomic mass of a given element is almost equal to its mass number. Standard atomic weight is used to give the value of the mean of the atomic masses in a mixture of isotopes in a given sample of an element.
Open navigation menu. Close suggestions Search Search. User Settings. Skip carousel. Carousel Previous. Carousel Next.
Approx atomic mass of first 30 elements
The atomic mass in Chemistry is the average mass of the atoms of an element measured in atomic mass units amu. The atomic mass is simply defined as the weighted average of all of the isotopes of an element, in which the mass of each isotope is multiplied by the abundance of that particular isotope. An interesting point to note is that it is also referred to as atomic weight. In this article, we will learn about the following things: the atomic mass of elements in detail, what is the atomic mass of all elements, and what is the atomic number and atomic mass of elements. Since we have seen the definition of atomic mass let us discuss it in detail. The atomic mass of a solitary atom is its absolute mass and is regularly expressed in atomic mass units or amu. For example, a normal carbon atom with six neutrons and six protons is denoted as carbon It has an atomic mass equal to 12 amu. The atomic mass number is usually rounded off to the nearest whole number. Since an element's isotopes have distinctive atomic masses, researchers may likewise decide the general atomic mass—once in a while called the atomic weight—for an element. The general atomic mass is the normal of the atomic masses of the apparent multitude of various isotopes in an example. Every isotope's contribution to the normal is controlled by how huge a fraction of the example it makes up.
This relationship helps simplify calculations and understanding of atomic masses.
Atomic mass is the total mass of all subatomic particles of an atom, including protons, neutrons, and electrons. One dalton is equivalent to one-twelfth of the mass of a carbon atom at rest in its ground state. This definition provides a standard reference point for measuring atomic masses. The atomic mass of an individual atom is closely related to its mass number, which represents the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. This relationship helps simplify calculations and understanding of atomic masses.
For example, magnesium exists as a mixture of three isotopes, each with an atomic number of 12 and with mass numbers of 24, 25, and 26, respectively. These isotopes can be identified as 24 Mg, 25 Mg, and 26 Mg. They differ only because a 24 Mg atom has 12 neutrons in its nucleus, a 25 Mg atom has 13 neutrons, and a 26 Mg has 14 neutrons. Note that in addition to standard names and symbols, the isotopes of hydrogen are often referred to using common names and accompanying symbols. Hydrogen-2, symbolized 2 H, is also called deuterium and sometimes symbolized D. Hydrogen-3, symbolized 3 H, is also called tritium and sometimes symbolized T. Use this Build an Atom simulator to build atoms of the first 10 elements, see which isotopes exist, check nuclear stability, and gain experience with isotope symbols. Because each proton and each neutron contribute approximately one amu to the mass of an atom, and each electron contributes far less, the atomic mass of a single atom is approximately equal to its mass number a whole number. However, the average masses of atoms of most elements are not whole numbers because most elements exist naturally as mixtures of two or more isotopes.
Approx atomic mass of first 30 elements
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Elements and atoms. Fundamental properties of atoms including atomic number and atomic mass. The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom, and isotopes have the same atomic number but differ in the number of neutrons. Radioactivity pops up fairly often in the news. For instance, you might have read about it in discussions of nuclear energy, the Fukushima reactor tragedy, or the development of nuclear weapons. But what exactly does it mean for something to be radioactive?
Nerf hearthstone
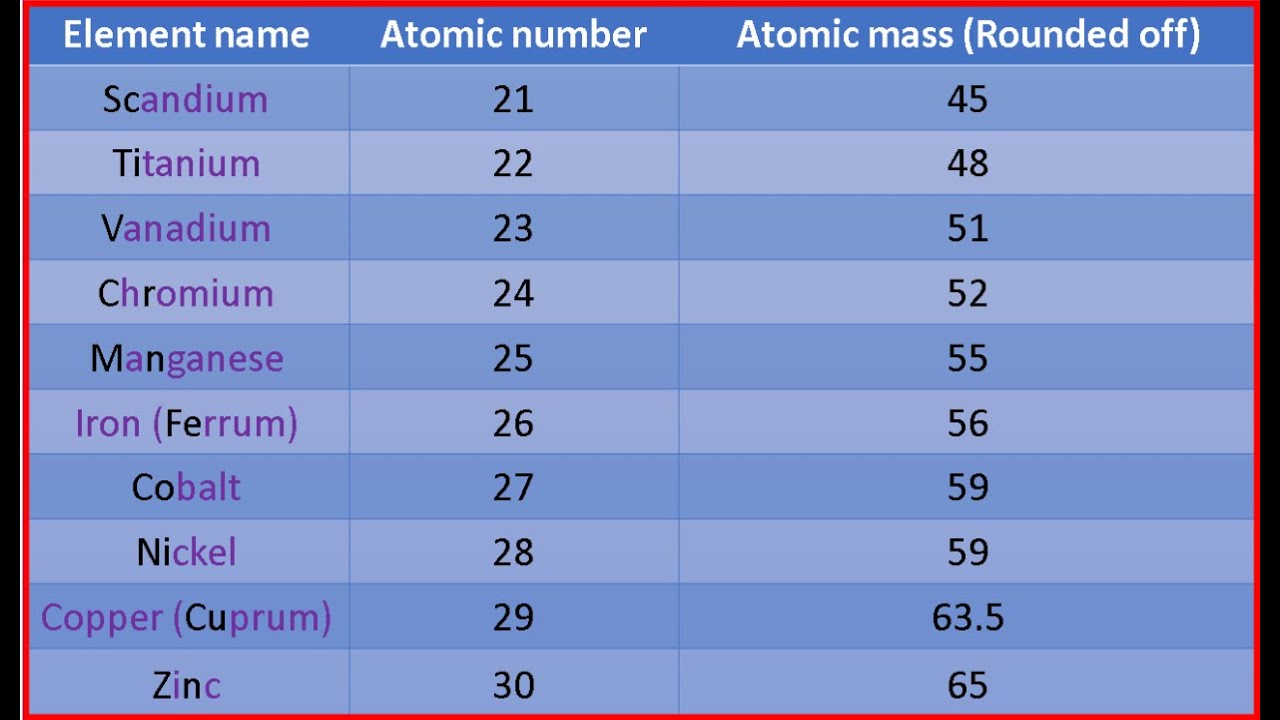
Here is the table showing the first 30 elements of the periodic table with their atomic masses and atomic number:. The letter Z is used for representing the atomic number. Nice works to help children to study online as to clear the doubts on any topic. Neutrons are uncharged subatomic particles which are stable when bound in an atomic nucleus. Improve Improve. Molarity Molality Normality. The atomic number is important because the number of protons determines the number of electrons that surround the nucleus. Professional Documents. The atomic mass of a solitary atom is its absolute mass and is regularly expressed in atomic mass units or amu. Similar Reads. What is the full form of amu? Atomic mass cannot be used for defining the type of element.
As early chemists worked to purify ores and discovered more elements, they realized that various elements could be grouped together by their similar chemical behaviors. One such grouping includes lithium Li , sodium Na , and potassium K : These elements all are shiny, conduct heat and electricity well, and have similar chemical properties.
Atomic Mass Atomic Mass. The formula to determine the mass number of an atom of a specific element is given by :. Carousel Next. The table includes common elements such as hydrogen, helium, carbon, oxygen, sodium, magnesium, and zinc. Shivprasad Ashtikar July 27, at pm. Avi Jaiswal September 3, at am. Adenike nikky November 27, at am. What are Monovalent Ions? What kind of Experience do you want to share? The atomic mass of oxygen is approximately The averaging procedure also involves taking into consideration the abundance of each isotope and multiplying it with the mass of each. Since many elements exist as a mixture of isotopes, each with its own mass and abundance, the fractional atomic mass provides a weighted average of these isotopic masses. Get paid for your published articles and stand a chance to win tablet, smartwatch and exclusive GfG goodies! This was the atomic mass of the first 30 elements.

Speak directly.
Also that we would do without your remarkable idea
Bravo, brilliant idea