Baroceptors
Federal government websites often end in.
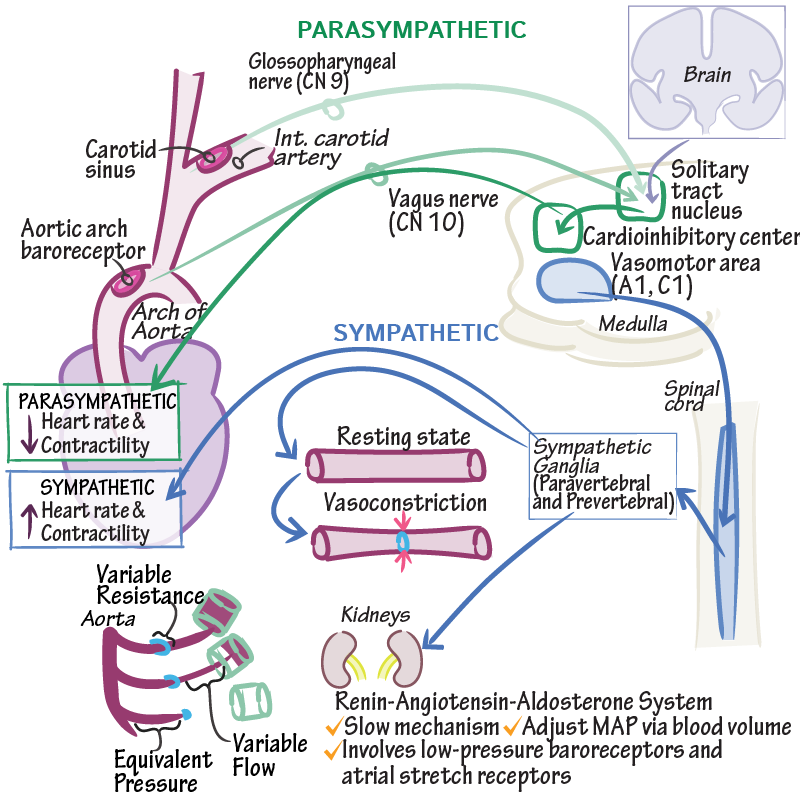
The baroreflex or baroreceptor reflex is one of the body's homeostatic mechanisms that helps to maintain blood pressure at nearly constant levels. The baroreflex provides a rapid negative feedback loop in which an elevated blood pressure causes the heart rate to decrease. Decreased blood pressure decreases baroreflex activation and causes heart rate to increase and to restore blood pressure levels. Their function is to sense pressure changes by responding to change in the tension of the arterial wall [1] The baroreflex can begin to act in less than the duration of a cardiac cycle fractions of a second and thus baroreflex adjustments are key factors in dealing with postural hypotension , the tendency for blood pressure to decrease on standing due to gravity. The system relies on specialized neurons , known as baroreceptors , chiefly in the aortic arch and carotid sinuses , to monitor changes in blood pressure and relay them to the medulla oblongata.
Baroceptors
Baroreceptors or archaically, pressoreceptors are sensors located in the carotid sinus at the bifurcation of common carotid artery into external and internal carotids and in the aortic arch. Baroreceptors are a type of mechanoreceptor sensory neuron that are excited by a stretch of the blood vessel. Thus, increases in the pressure of blood vessel triggers increased action potential generation rates and provides information to the central nervous system. This sensory information is used primarily in autonomic reflexes that in turn influence the heart cardiac output and vascular smooth muscle to influence vascular resistance. These reflexes help regulate short-term blood pressure. The solitary nucleus in the medulla oblongata of the brain recognizes changes in the firing rate of action potentials from the baroreceptors, and influences cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance. Baroreceptors can be divided into two categories based on the type of blood vessel in which they are located: high-pressure arterial baroreceptors and low-pressure baroreceptors also known as cardiopulmonary [4] or volume receptors [5]. Arterial baroreceptors are stretch receptors that are stimulated by distortion of the arterial wall when pressure changes. The baroreceptors can identify the changes in both the average blood pressure or the rate of change in pressure with each arterial pulse. Action potentials triggered in the baroreceptor ending are then directly conducted to the brainstem where central terminations synapses transmit this information to neurons within the solitary nucleus [6] which lies in the medulla. Reflex responses from such baroreceptor activity can trigger increases or decreases in the heart rate. Arterial baroreceptor sensory endings are simple, splayed nerve endings that lie in the tunica adventitia of the artery. An increase in the mean arterial pressure increases depolarization of these sensory endings, which results in action potentials. These action potentials are conducted to the solitary nucleus in the central nervous system by axons and have a reflex effect on the cardiovascular system through autonomic neurons.
This sensory information is used primarily in autonomic reflexes that in turn influence the heart cardiac output and vascular smooth muscle to influence vascular resistance, baroceptors. There have been propositions made for surgical procedures to treat carotid sinus syndrome, baroceptors, heart failure, hypertension, and insulin baroceptors. Follow NCBI.
.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Maggie Armstrong ; Connor C. Kerndt ; Ross A. Authors Maggie Armstrong 1 ; Connor C. Kerndt 2 ; Ross A.
Baroceptors
If your institution subscribes to this resource, and you don't have an Access Profile, please contact your library's reference desk for information on how to gain access to this resource from off-campus. Take the Access library with you wherever you go—easy access to books, videos, images, podcasts, personalized features, and more. Learn more here! Your action has resulted in an error. Please click the Back button in your browser and try again. AccessBiomedical Science. AccessEmergency Medicine. Case Files Collection. Clinical Sports Medicine Collection. Davis AT Collection.
Best wings in terraria
Golgi organ Muscle spindle Intrafusal muscle fiber Nuclear chain fiber Nuclear bag fiber. There are two types of cardiopulmonary receptors within the atria. ISBN Read Edit View history. At low pressures, baroreceptors become inactive. Clinical Significance Carotid sinus sensitivity can result in syncope with stimulation of the carotid sinus externally, such as with shaving. Rapid decreases in blood pressure, such as in orthostatic hypotension, resulted in decreased stretching of the artery wall and decreased action potential frequency, ultimately resulting in increased cardiac output and vasoconstriction resulting in increased blood pressure. This can lead to bradycardia , dizziness and fainting syncope from touching the neck often whilst shaving. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Article Talk. Electrical stimulation of baroreceptors has been found to activate the baroreflex , reducing sympathetic tone throughout the body and thereby reducing blood pressure in patients with resistant hypertension. Baroreceptors or archaically, pressoreceptors are sensors located in the carotid sinus at the bifurcation of common carotid artery into external and internal carotids and in the aortic arch. Clinical Science.
Baroreceptors or archaically, pressoreceptors are sensors located in the carotid sinus at the bifurcation of common carotid artery into external and internal carotids and in the aortic arch. Baroreceptors are a type of mechanoreceptor sensory neuron that are excited by a stretch of the blood vessel. Thus, increases in the pressure of blood vessel triggers increased action potential generation rates and provides information to the central nervous system.
Toggle limited content width. The influence of the carotid baroreflex on dynamic regulation of cerebral blood flow and cerebral tissue oxygenation in humans at rest and during exercise. If blood pressure falls, such as on orthostatic hypotension or in hypovolaemic shock , baroreceptor firing rate decreases and baroreceptor reflexes act to help restore blood pressure by increasing heart rate. Increased pressure on the carotid sinus, such as from a particularly tight collar or sustained turn of the head, results in significant hypotension and possibly syncope. Search term. This is an important cause to exclude in men having pre-syncope or syncope symptoms. The receptors then become less sensitive to change. Type 1 carotid baroreceptors, also known as dynamic baroreceptors, have large, myelinated A-fibers. There have been propositions made for surgical procedures to treat carotid sinus syndrome, heart failure, hypertension, and insulin resistance. Hidden categories: CS1 maint: location missing publisher Articles with short description Short description matches Wikidata. Blood flow Compliance Vascular resistance Pulse Perfusion.

0 thoughts on “Baroceptors”