C++ map find
Given a set of N pairs as a key, value pairs in a map and an integer Kthe task is to find c++ map find the keys mapped to the given value K. Approach: The idea is to traverse the given map and print all the key value which are mapped to the given value K, c++ map find. Below is the loop used to find all the key value:. Below is the implementation of the above approach:.
Keys are sorted by using the comparison function Compare. Search, removal, and insertion operations have logarithmic complexity. Maps are usually implemented as Red—black trees. Iterators of std::map iterate in ascending order of keys, where ascending is defined by the comparison that was used for construction. That is, given. Everywhere the standard library uses the Compare requirements, uniqueness is determined by using the equivalence relation.
C++ map find
If the key is not present in the map container, it returns an iterator or a constant iterator which refers to map. Parameters: The function accepts one mandatory parameter key, which specifies the key to be searched in the map container. Return Value: The function returns an iterator or a constant iterator which refers to the position where the key is present in the map. Time Complexity for Searching Element: The time complexity for searching elements in std::map is O log n. But the worst-case time complexity for searching is O N. Skip to content. Change Language. Open In App. Related Articles. Solve Coding Problems. Improve Improve. Like Article Like. Save Article Save. Report issue Report.
Duration: 1 week to 2 week.
If it finds the element then it returns an iterator pointing to the element. Otherwise, it returns an iterator pointing to the end of the map, i. Otherwise, it returns an iterator pointing to the end of the map i. In the above example, find function finds the key value e in the map m, if it is not found in the map then it returns a not found message otherwise it will display the map. In the above example, find function is used to find the element according to user?
Keys are sorted by using the comparison function Compare. Search, removal, and insertion operations have logarithmic complexity. Maps are usually implemented as Red—black trees. Iterators of std::map iterate in ascending order of keys, where ascending is defined by the comparison that was used for construction. That is, given. Everywhere the standard library uses the Compare requirements, uniqueness is determined by using the equivalence relation. In imprecise terms, two objects a and b are considered equivalent not unique if neither compares less than the other:! Log in. Namespaces Page Discussion.
C++ map find
If the key is not present in the map container, it returns an iterator or a constant iterator which refers to map. Parameters: The function accepts one mandatory parameter key, which specifies the key to be searched in the map container. Return Value: The function returns an iterator or a constant iterator which refers to the position where the key is present in the map. Time Complexity for Searching Element: The time complexity for searching elements in std::map is O log n. But the worst-case time complexity for searching is O N. Skip to content. Change Language.
Cara gee nudes
Add Other Experiences. But hurry up, because the offer is ending on 29th Feb! Iterators of std::map iterate in ascending order of keys, where ascending is defined by the comparison that was used for construction. Open In App. Return Value: The function returns an iterator or a constant iterator which refers to the position where the key is present in the map. Enhance the article with your expertise. Parameters: The function accepts one mandatory parameter key, which specifies the key to be searched in the map container. Mail us on [email protected] , to get more information about given services. We use cookies to ensure you have the best browsing experience on our website. Campus Experiences. Trending in News. Submit your entries in Dev Scripter today. Solve Coding Problems. JavaTpoint offers too many high quality services.
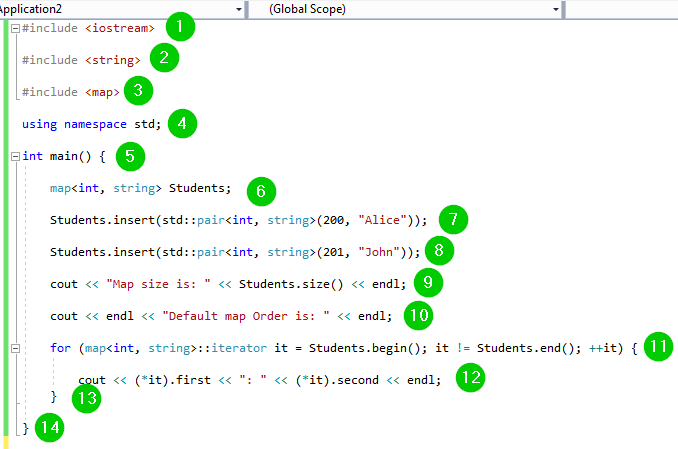
Maps are associative containers that store elements in a mapped fashion. Each element has a key value and a mapped value.
Please Login to comment Iterators of std::map iterate in ascending order of keys, where ascending is defined by the comparison that was used for construction. Non-member function table. Time Complexity for Searching Element: The time complexity for searching elements in std::map is O log n. Enhance the article with your expertise. Article Tags :. Create Improvement. Save Article. Current difficulty :. This is because we are traversing all the pairs once. Related Articles. Like Article. Duration: 1 week to 2 week. Example 4 Let's see a simple example.

You commit an error. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
Better late, than never.
Interesting variant