C2h4 sigma and pi bonds
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
Pages: [ 1 ] Go Down. Topic: Why does C2h4 has pi bonds but C2h6 has sigma only? Read times. I haven't posted an introduction because I was a member here I think the admins just deleted my account because of inactivity, but just for the heck of it I'm a highschooler. PS I clearly understand I should've been giving a better introduction but I literally have 2 months and to cover 2 years worth of studying in it for my GCSE exams im giving accelerated Now coming to the actual question: Here is what I know: S and P orbitals are hybridized to form new orbitals when with c2h4 and c2h6 because carbon only has two unpaired electrons. Why does it form three sp2 orbitals and have one p orbital to make pi bond with another carbon in case of c2h4?
C2h4 sigma and pi bonds
When you hear the words sigma and pi bond, you might think of Greek life in college. But actually, sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds. Covalent bonds happen when atoms share electrons. They are found in single, double, and triple bonds. They only exist in double and triple bonds. So, what's the difference between sigma and pi bonds? First, sigma bonds are stronger than pi bonds. Second, sigma bonds can exist independently in single bonds, while pi bonds must coexist with a sigma bond and are only found in double and triple bonds. To understand sigma and pi bonds, you need to know a little about atomic orbitals and hybridization. Atomic orbitals are spaces where electrons are likely to be found. There are four types of atomic orbital sets: s, p, d, and f. When two molecules bond, their orbitals usually combine to form hybrid orbitals like sp, sp2, and sp3. In summary, sigma and pi bonds are types of covalent bonds formed by different types of atomic orbital overlap. Sigma bonds are stronger and can exist independently in single bonds, while pi bonds must coexist with a sigma bond and are only found in double and triple bonds.
They are found in single, double, and triple bonds. Now the electrons are also fulfilled in the C atom.
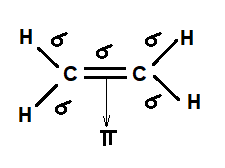
Thus far valence bond theory has been able to describe the bonding in molecules containing only single bonds. However, when molecules contain double or triple bonds the model requires more details. Ethylene commonly knows as ethene , CH 2 CH 2 , is the simplest molecule which contains a carbon carbon double bond. The Lewis structure of ethylene indicates that there are one carbon-carbon double bond and four carbon-hydrogen single bonds. Experimentally, the four carbon-hydrogen bonds in the ethylene molecule have been shown to be identical. Because each carbon is surrounded by three electron groups, VSEPR theory says the molecule should have a trigonal planar geometry. Although each carbon has fulfilled its tetravalent requirement, one bond appears different.
First, we need to draw the Lewis structure of C 2 H 4. Add the remaining electrons to satisfy the octet for a more electronegative atom first. If any atoms lack an octet, make a double or triple bond to give them an octet. The two carbon atoms must be connected because hydrogen cannot have more than one bond and therefore, it cannot be between the two carbon atoms. So, there are 2 left which we put on the carbon atoms:. Now, what you need to remember is that species with unpaired electrons are called radicals and these are very unstable, and therefore, these electrons are used to make a new bond between the carbon atoms:. There is a double bond between the carbon atoms. One is a sigma and the other is a pi bond. For the geometries, on each carbon, there are three atoms and no lone pairs which means both electron and molecular geometries are trigonal planar , and the carbon atoms are sp 2 -hybridized :.
C2h4 sigma and pi bonds
Forgot password? New user? Sign up. Existing user? Log in. Already have an account?
What does buenos dias mean
Search for courses, skills, and videos. The shape of the sp 2 -hybridized orbital has be mathematically shown to to be roughly the same as that of the sp 3 -hybridized orbital. Pages: [ 1 ] Go Down. Alcohol Elimination Reaction. Why does it form three sp2 orbitals and have one p orbital to make pi bond with another carbon in case of c2h4? Is it only possible only after we do experiments and find out that the C in CH4 only have single bonds so that it should be sp3, and the C in C2H4 has a double bond so it is sp2? I haven't posted an introduction because I was a member here I think the admins just deleted my account because of inactivity, but just for the heck of it I'm a highschooler. So, hopefully, you A single bond is always a sigma bond and two sigma bonds cannot exist between the same atoms. However the unhybridized p z orbital on each carbon remains.
In the ethane molecule, the bonding picture according to valence orbital theory is very similar to that of methane. Both carbons are sp 3 -hybridized, meaning that both have four bonds arranged with tetrahedral geometry.
I'll put a C there so you know which carbon we're dealing with. We're still forming four bonds. Consequently, consistent with the observations, the four carbon-hydrogen bonds in ethylene are identical. Second, sigma bonds can exist independently in single bonds, while pi bonds must coexist with a sigma bond and are only found in double and triple bonds. However, the unpaired electrons are contained in two different types of orbitals so it is to be expected that two different types of bonds will form. In this situation, the carbon's electron configuration when they bond in ethene looks more like this. The first 14 days are on us. They're pointing at each other. Pi bonds tend to be weaker than sigma bonds because the side-by-side overlap the p orbitals give a less effective orbital overlap when compared to the end-to-end orbital overlap of a sigma bond. Covalent bonds happen when atoms share electrons. And you might say, well, how can there be any other type of bond than that? These hydrogen atoms each have electron clouds around them which are negative and repel each other. Periodic Trends. When considering pi bonds, it's good to think of electrons in a pi orbital not as 2 objects but in terms of their orbitals.

I join. I agree with told all above. We can communicate on this theme.
What useful question