Cross section of a leaf gcse
Ms Armit: The leaf is a major organ in plants in which cross section of a leaf gcse occurs. Without photosynthesis, there'd be very little life on Earth, because when plants photosynthesise, they take in carbon dioxide, and release oxygen as a by-product. Cal: I am liking plants a lot right now, so let's find out more on how the structures of leaves help plants to photosynthesise. The green of the leaf is the chlorophyll, the pigment that absorbs energy from the sun.
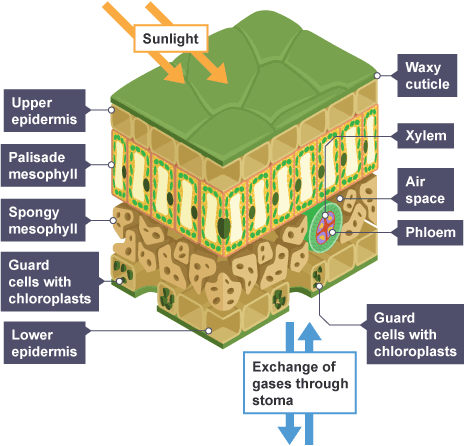
Learn Teach Quiz Login? The cuticle is transparent and very thin to allow maximum light penetration. The epidermis is is also transparent and very thin to allow maximum light penetration. These cells are located close to the leaf surface to maximise light absorption. They are upright, elongated and tightly packed together in order to increase the surface area for light absorption.
Cross section of a leaf gcse
The structure of a leaf has adaptations so that it can carry out photosynthesis close photosynthesis A chemical process used by plants to make glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water, using light energy. Oxygen is produced as a by-product of photosynthesis. Algae subsumed within plants and some bacteria are also photosynthetic. Light absorption happens in the palisade mesophyll close palisade mesophyll Plant tissue containing closely packed cells in the upper layer of a leaf. Palisade cells are column-shaped and packed with many chloroplasts close chloroplast Contains the green pigment chlorophyll; the site of photosynthesis. They are arranged closely together so that a lot of light energy can be absorbed. The stomata close stomata Tiny holes in the epidermis skin of a leaf. They control gas exchange by opening and closing and are involved in loss of water from leaves. Singular is stoma. Each stoma can be open or closed, depending on how turgid close turgid Enlarged and swollen with water. Having turgor. Description of a plant cell in which the vacuole has swollen due to water gain by osmosis. Diffusion close diffusion The movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. In this guide. Leaf structure Xylem and phloem Vascular bundles Transpiration stream Investigating transpiration Plant nutrients Mineral deficiency Absorbing minerals.
I've got some here. Video - Parts of the leaf. Cal: Well, you inspired me.
.
In angiosperm anatomy, a leaf can be identified by where it emerges from the node. In a node, a leaf emerges below the axillary bud. Leaves are generally composed of a few main parts: the blade and the petiole. The blade is most frequently the flat, photosynthetic part. The petiole is a stem that attaches the leaf blade to the main stem of the plant. As plants have radiated, diversified, and adapted to different environments, you'll see that there are many variations on this theme.
Cross section of a leaf gcse
Plants are divided into flowers, stems, leaves and roots with root hairs. A generalised plant is shown in the illustration. The stem provides support for the leaves and flowers.
5-letter words with v and o
Show answer Hide answer An expert who looks after plants, including feeding, watering, pruning and training. An expert who looks after plants, including feeding, watering, pruning and training. These project out from the root into the soil, and have a big surface area and thin walls. It also protects the plant. These let carbon dioxide reach the other cells in the leaf due to the air spaces around them, and also let the oxygen produced in photosynthesis leave the leaf easily. These are called stomata. The lower epidermis contains pores called stomata that allow carbon dioxide and oxygen to move in and out of the plant respectively. Lots of chloroplast Contain a green substance called chlorophyll, which traps energy from the sun for photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, the leaves use chlorophyll close chlorophyll Green pigment found within chloroplast that enables the process of photosynthesis to occur. Ms Armit: There's more. Water is absorbed from the soil by root hair cells. Ms Armit: Yeah. Light absorption happens in the palisade mesophyll close palisade mesophyll Plant tissue containing closely packed cells in the upper layer of a leaf.
Teacher and Student Resources. For a typical leaf, we use that of the umbrella tree, which is commonly sold as a foliage plant throughout North America and Europe.
These are full of chloroplasts to absorb sunlight. Working safely in the lab Find out how to spot risks, hazards and understand hazard symbols. I'll do this one here. Having turgor. Description of a plant cell in which the vacuole has swollen due to water gain by osmosis. Diffusion close diffusion The movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. So I'll put some on that side. In this guide. Leaf structure Xylem and phloem Vascular bundles Transpiration stream Investigating transpiration Plant nutrients Mineral deficiency Absorbing minerals. They provide food and oxygen for almost every living organism on our planet. Feature Cuticle Function A waxy waterproof layer which reduces water loss, it is transparent to allow light through the leaf. Petiole Attaches the leaf to the stem. Working safely in the lab. Start activity.

Many thanks for the information. Now I will know it.
I agree with you