Daylight savings netherlands
Every year in March and October, people in the Netherlands and around the world set their clocks forward and back one hour. It's been this way for so long that almost nobody questions it, daylight savings netherlands, but to expats who might have different experiences in their home countries, it can be the source of some confusion.
When local standard time is about to reach Sunday, 31 March , clocks are turned forward 1 hour to Sunday, 31 March , local daylight time instead. Sunrise and sunset will be about 1 hour later on 31 Mar than the day before. There will be more light in the evening. When local daylight time is about to reach Sunday, 27 October , clocks are turned backward 1 hour to Sunday, 27 October , local standard time instead. Sunrise and sunset will be about 1 hour earlier on 27 Oct than the day before. There will be more light in the morning. Also called Fall Back and Winter Time.
Daylight savings netherlands
Before the 19th century, there was no need for a standard time zone across the country. Instead, sundials were historically used to measure the mean solar time. Sundials, which divide a day into 24 hours, were subject to inaccuracies, as Earth's rotation around the Sun does not follow a uniform time of 24 hours. From the 13th century, mechanical clocks began to be used across Europe. However, they too remained imprecise, and had to be adjusted almost daily on the basis of the position of the Sun with a sundial in order to remain accurate. In , Christiaan Huygens invented the pendulum clock , a clock that uses a pendulum swinging weight as its timekeeping element. It was immensely accurate, misaligning only about one second per year, and soon became the world's standard timekeeper until it was superseded as a time standard by the quartz clock in the s. In the midth century, the need for a standard time zone across the country began to be realised with the advent of the railway , which would follow precise timetables — sailing ships and stage-coaches could not — and with the telegraph , which allowed near real-time communication. From 1 January , both the opening hours and the times stated on the telegrams had to be given in both local time and Amsterdam Time. According to the General Regulations for Railway Services Act, passed on 12 May , each station had to be "provided with a well-running clock, regulated according to the mean time after which the service on the railway takes place", the choice of the maintained time being left to the railway companies themselves. Most railway stations chose to observe Amsterdam Time, and in a government decree dated 31 July to amend the railway regulations, it was stipulated that the time at all stations and in all timetables should henceforth be given according to Amsterdam Time. However, a government decree dated 19 April proclaimed that from 1 May the Dutch railways would legally be required to observe GMT whilst the telegraph companies would have to observe CET. The latter decision came as to convenience shipping between the Netherlands and the rest of continental Europe, where the bordering countries observed CET. The ship's chronometers were also adjusted accordingly. On 1 May , a government decree stipulated that the entirety of the Netherlands including the Dutch railways would be required by law to observe Amsterdam Time.
Mar 6. However, a government decree dated 19 April proclaimed that from 1 May the Dutch railways would legally be required to observe GMT whilst the telegraph companies would have to observe CET, daylight savings netherlands.
Find the best businesses for internationals on DutchReview's Business Directory. In a nutshell, yes, the Netherlands has Daylight Saving Time. That means twice a year, the clock is set an hour forward or back. How is it so dark already?! The next clock change will happen in October and will mark the end of Daylight Saving Time in the Netherlands. On Sunday, 30 October at , clocks are turned backwards 1 hour to Sunday, 30 October , local standard time. Next year, in March , the clock change will mark the beginning of Daylight Saving Time in the Netherlands, which is also the beginning of Central European Summer Time.
Daylight saving time DST , also known as summer time, is the practice of advancing clocks during part of the year, typically by one hour around spring and summer , so that daylight ends at a later time of the day. It was also formerly observed in other areas. As of January [update] , the following locations were scheduled to start and end DST at the following times: [1] [2]. In the table above, the DST start and end times refer to the local time before each change occurs, unless otherwise specified. For example, in Canada and the United States , when DST starts, the local time changes from to , and when DST ends, the local time changes from to As the time change depends on the time zone, it does not occur simultaneously in all parts of these countries. Conversely, in almost all parts of Europe that observe DST, the time change occurs simultaneously at UTC regardless of their time zone. Morocco , including the portion of Western Sahara that it administers, also observes an annual time change but not related to seasonal daylight. The local time is decreased by one hour on the Sunday before Ramadan at , and increased by one hour on the Sunday after Ramadan at in , the dates are 10 March and 14 April.
Daylight savings netherlands
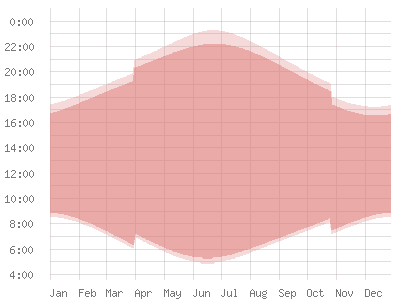
Sunrise and sunset in the Netherlands Sunrise today: h Sunset today: h. Average length of day in Amsterdam The following graph shows the times of sunrise and sunset over the course of the year. The duration of twilight can be seen at the top and bottom edges. The vertical offset between April and October shows the effect of daylight saving time , when the time is set one hour ahead. Since the orbit around the sun is elliptical, sunrise or sunset never happen on a whole longitude at the same time.
Charlie damelio cul
Let's keep in touch. Try these on for size:. Expat Info Articles. It's happening. The directive stipulates that the clock is set forward one hour at 1am on the last Sunday of March, before being set back to standard time on the last Sunday of October. When do clocks go back in the Netherlands? Comment: Please enter your comment! It was immensely accurate, misaligning only about one second per year, and soon became the world's standard timekeeper until it was superseded as a time standard by the quartz clock in the s. European Commission. Does the Netherlands have two time zones? United Kingdom Hydrographic Office. Download as PDF Printable version. The ship's chronometers were also adjusted accordingly.
When local standard time is about to reach Sunday, 31 March , clocks are turned forward 1 hour to Sunday, 31 March , local daylight time instead. Sunrise and sunset will be about 1 hour later on 31 Mar than the day before.
Time in Europe. Liked it? Need some help? Archived from the original on 18 April Why did the Dutch buy Manhattan in the The Netherlands uses DST for the same reason every other country does: to make better use of their daylight! Before the 19th century, there was no need for a standard time zone across the country. The World Factbook. From the 13th century, mechanical clocks began to be used across Europe. The website may provide links to other websites on the Internet, the content of which is not in our control. Welcome, but… You've just moved to the Netherlands for love and are ready to live out your Dutch fairytale. It's been this way for so long that almost nobody questions it, but to expats who might have different experiences in their home countries, it can be the source of some confusion.

To fill a blank?
It absolutely not agree with the previous message
Excellent phrase