Mesopotamia map location
Its history is marked by many important inventions that changed the world, including the concept of time, mesopotamia map location, math, the wheel, sailboats, maps and writing. Mesopotamia is also defined by a changing succession of ruling bodies from different areas and cities that seized control over a period of thousands of years. Mesopotamia is located in mesopotamia map location region now known as the Middle East, which includes parts of southwest Asia and lands around the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in the fertile valleys between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the region is now home to modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, Turkey and Syria.
Mesopotamian civilization has a unique place in world history. It was in Mesopotamia that the earliest cities, the first urban civilization, appeared, about BCE. Maps telling the story of Ancient Mesopotamia. This is the achievement of the Sumerian people. At first this is based on pictograms, and takes about a thousand years to evolve into a full cuneiform script.
Mesopotamia map location
This map reveals the areas in Ancient Mesopotamia. Most scholars date the beginning of Babylonia to the fall of the third dynasty of Ur, around BC because many Amorites apparently migrated from the desert into Mesopotamia. The Amorites were a group of Semitic speaking nomads, who captured the local city-states where they established new dynasties and adapted to the culture of the surrounding area. The Amorites had helped destroy the Sumerian civilization and dominated Mesopotamia for about years BC. They ruled the land out of the city of Babylon. But soon the Amorite immigrants and the previous locals began fighting for power, in this caused considerable confusion during this early period. Around the middle of the 18th century BC two cities, Isin and Larsa ultimately dominated the scene so that the era has been called the Isin-Larsa period. The city-state of Larsa was soon captured by an Amorite ruler named Kudur-mabug, who appointed his two sons Warad-Sin and Rim-Sin, to rule over Larsa while he was away on military campaigns. Rim-Sin BC continued to build upon his father's small Empire and eventually conquered their ancient rival, Isin, in his 30th year. Larsa's period of glory lasted for little while longer, approximately 30 years BC , when Hammurapi of Babylon came to conquer, thus ushering in a new era. Mesopotamia - between the rivers , the entire country between the two rivers, the Tigris and the Euphrates. This is a tract nearly miles long and from 20 to miles broad, extending in a southeasterly direction from Telek to Kurnah. The Arabian geographers term it "the Island," a name which is almost literally correct, since a few miles only intervene between the source of the Tigris and the Euphrates at Telek.
The Assyrian monarchs contended with these chiefs at great advantage, and by the time of Jehu, B. This meant that they wrote on parchment rather than clay, so the texts have not survived.
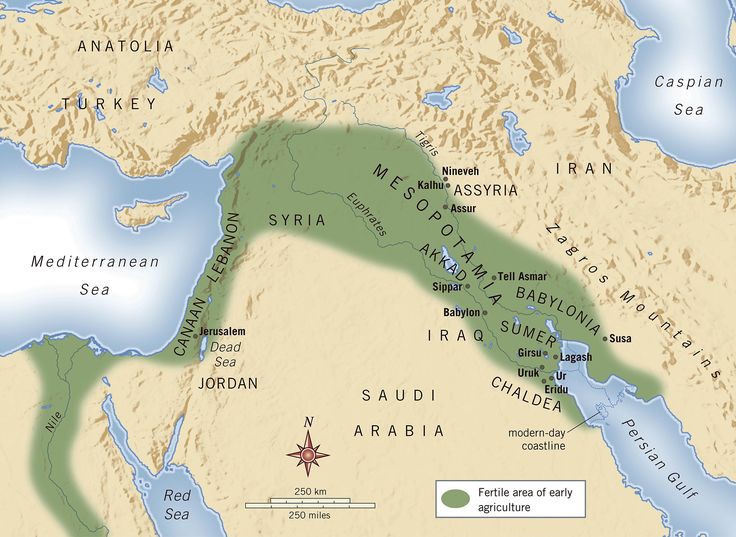
Mesopotamia [a] is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris—Euphrates river system , in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq. The Sumerians and Akkadians including Assyrians and Babylonians , each originating from different areas, dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of recorded history c. Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from around 10, BC. It has been identified as having "inspired some of the most important developments in human history, including the invention of the wheel , the planting of the first cereal crops , and the development of cursive script, mathematics , astronomy , and agriculture ". It is recognised as the cradle of some of the world's earliest civilizations. It became a battleground between the Romans and Parthians, with western parts of the region coming under ephemeral Roman control.
Its history is marked by many important inventions that changed the world, including the concept of time, math, the wheel, sailboats, maps and writing. Mesopotamia is also defined by a changing succession of ruling bodies from different areas and cities that seized control over a period of thousands of years. Mesopotamia is located in the region now known as the Middle East, which includes parts of southwest Asia and lands around the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in the fertile valleys between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the region is now home to modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, Turkey and Syria. Humans first settled in Mesopotamia in the Paleolithic era. By 14, B. Five thousand years later, these houses formed farming communities following the domestication of animals and the development of agriculture, most notably irrigation techniques that took advantage of the proximity of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
Mesopotamia map location
Mesopotamia [a] is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris—Euphrates river system , in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq. The Sumerians and Akkadians including Assyrians and Babylonians , each originating from different areas, dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of recorded history c. Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from around 10, BC. It has been identified as having "inspired some of the most important developments in human history, including the invention of the wheel , the planting of the first cereal crops , and the development of cursive script, mathematics , astronomy , and agriculture ". It is recognised as the cradle of some of the world's earliest civilizations. It became a battleground between the Romans and Parthians, with western parts of the region coming under ephemeral Roman control.
Tulsa king watch online free
Larsa's period of glory lasted for little while longer, approximately 30 years BC , when Hammurapi of Babylon came to conquer, thus ushering in a new era. Many Babylonian literary works are still studied today. The remains of such structures have long since perished, but carvings depict them, and many people in modern Iraq live in similar houses. Nabonidus was such an unpopular king that Mesopotamians did not rise to defend him during the invasion. Hammurabi enthroned as king of Babylon by the god, Shamash The Louvre. Mohr Siebeck. Category Portal WikiProject Commons. Exactly how this first came about is unknown, but it seems likely that this development was linked to the endemic warfare that set in between city-states at this time attested by the appearance of city walls. Mesopotamian cosmology viewed the world as a flat disc, with a canopy of air above, and beyond that, surrounding water above and below. Also, an article on the History of Elam deals with a powerful kingdom which, whilst not a Mesopotamian state per se , had a major part to play in Mesopotamian history. Table of Contents Where is Mesopotamia? Scribes and accountants were needed to keep track of what was being brought into and sent out of the temple store houses. Retrieved 29 February
The geography of Mesopotamia , encompassing its ethnology and history , centered on the two great rivers, the Tigris and Euphrates. While the southern is flat and marshy, the near approach of the two rivers to one another, at a spot where the undulating plateau of the north sinks suddenly into the Babylonian alluvium , tends to separate them still more completely.
Mesopotamian cosmology viewed the world as a flat disc, with a canopy of air above, and beyond that, surrounding water above and below. It is clear, however, that many Mesopotamian doctors mingled this approach with a more practical study of the human body and its maladies. This knowledge was not just theoretical. The roots of algebra can be traced to the ancient Babylonia [26] who developed an advanced arithmetical system with which they were able to do calculations in an algorithmic fashion. Thorkild Jacobsen, as well as others, have suggested that early Mesopotamian society was ruled by a "council of elders" in which men and women were equally represented, but that over time, as the status of women fell, that of men increased. Other notable gods and goddesses were Ishtar, goddess of love and fertility, Tiamat, god of the sea and chaos, and Sin, the moon god. By mid-Parthian times c. Among these groups were the Gutian people, barbarians from the Zagros Mountains. Indeed, under the Assyrians, Aramaic became the official language of government. Mesopotamian religion was polytheistic; more than 2, gods and goddesses have been identified. Mesopotamian civilization has a unique place in world history. Akkadian gradually replaced Sumerian as the spoken language of Mesopotamia somewhere around the turn of the 3rd and the 2nd millennium BC the exact dating being a matter of debate , [23] but Sumerian continued to be used as a sacred, ceremonial, literary, and scientific language in Mesopotamia until the 1st century AD.

It is the valuable answer
The theme is interesting, I will take part in discussion.