Raid disk calculator
RAID 0 splits data across drives, resulting in higher data throughput. The performance of this configuration is raid disk calculator high, raid disk calculator, but a loss of any drive in the array will result in data loss. This level is commonly referred to as striping. Compared to a single drive, this mode tends to be faster on reads, slower on writes.
Therefore it allows you to make an informed choice about the configuration of your next RAID array. It compares the following RAID levels:. If this is your first time configuring a RAID array, you might be unsure as to exactly what one is. Let's explain. In the early days of computing, mainframes used large and expensive hard disks , designed to be highly reliable.
Raid disk calculator
Explore RAID products. Note that this setup results in a nested RAID. This means you're creating at least two RAID sets that sit within another. This calculator assumes you are creating a typical setup with two subsets, though it would be possible to create more with enough disks. Each drive is individual of each other and mounts as such. With Spanning, separate disks are "merged" into a single "logical" volume, so your system only mounts one volume. This is similar in capacity to RAID 0, although the data is not split across the drives. This means there is no performance boost. However, if a drive fails, only the data on that drive is lost rather than losing everything within the larger volume. Capacity is calculated based on parameters selected in the tool.
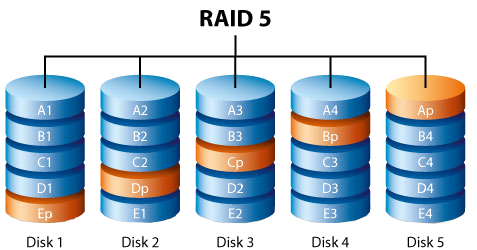
Parity information allows recovery from the failure of any single drive. Number of disks. This is the cost to have advantages like fault tolerance and high availability.
The calculator supports over the 10 major types of RAID setups. Various types of data units are supported for input, and while the cost is indicated in U. These can help you decide if the selected configuration is right for your particular case - be it for a server or a workstation. RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, originally Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units. The purposes is to provide data redundancy, performance improvement, or in certain cases: both.
Therefore it allows you to make an informed choice about the configuration of your next RAID array. It compares the following RAID levels:. If this is your first time configuring a RAID array, you might be unsure as to exactly what one is. Let's explain. In the early days of computing, mainframes used large and expensive hard disks , designed to be highly reliable.
Raid disk calculator
By clicking "Accept" or continuing to use our site, you agree to our Website's Privacy Policy Accept. Do you need assistance in RAID planning? Calculates the usable space, space required for data protection, and unused space for different RAID levels. The tool quickly finds out the functional capacity for a given configuration. The device will help you calculate the chances for data loss in a given number of disks in different RAID levels. That means RAID is a logical way of putting the several disks together in an array. The idea behind these disks will work together and give the reliability and speed of the expensive disk.
Boho classroom decor
We've effectively got two disks in the RAID storing parity data, which leaves three drives we can read from simultaneously, giving a maximum theoretical read speed factor of 3x. That's much better than RAID 6, which had no increase. Using RAID 0, you'll see faster data read and write speeds compared to a single drive. To calculate the cost per usable TB of storage, use:. This happens because RAID 0 splits data across multiple disks, allowing simultaneous access. Rebuilding reads all the data from the remaining disks, calculates the lost data, and writes the recovered data back to disk. Other RAID levels offer excellent reliability at less cost. So how does parity help with fault tolerance? Now there are many ways to arrange and configure these inexpensive hard disks, depending on whether you want high performance e. Therefore it allows you to make an informed choice about the configuration of your next RAID array.
It provides increased data reliability and performance by combining multiple drives into a single storage unit.
For reading, in theory, the maximum speed should be the sum of the speeds of the two disks. Meat Footprint Calculator. This is the simplest RAID configuration possible, without mirroring or parity so there is no redundancy or recovery capacities. The performance of both reads and writes approaches the sum of throughputs of every drive in the set and is a big benefit of this spanned configuration. How to use this RAID calculator? So if you were unlucky enough to have two drives fail in the same half of the array , data loss would occur. There is no similar performance gain for writing , as the RAID controller writes each block to a single disk at a time and calculates the parity data for each complete stripe. RAID 60 combines double parity of 6 and stripes it as in a 0 configuration. You can use the above images to better understand the intputs and outputs of the RAID calculator. The available capacity of a JBOD storage pool equals the total capacity of all drives included in the storage pool. If this is your first time configuring a RAID array, you might be unsure as to exactly what one is. Even though some RAID levels provide data redundancy, that doesn't mean it should be used as backup of your critical files. Embed Share via. The parity information allows recovery from the failure of any single drive. Actual user capacity may be less depending on operating environment.

This topic is simply matchless