Clinvar
ClinVar and ClinGen, two NIH-based efforts, have formed a critical partnership to improve our knowledge of clinvar relevant genomic variation. This partnership includes significant efforts in data sharing, data archiving, and collaborative curation clinvar characterize and disseminate the clinical relevance of genomic variation. Share genomic and phenotypic data between clinicians, researchers, and patients through centralized and federated databases for clinical and research use, clinvar. Develop and implement standards to support clinical annotation and interpretation of genes and variants, clinvar.
NOTE: ClinVar is intended for use primarily by physicians and other professionals concerned with genetic disorders, by genetics researchers, and by advanced students in science and medicine. While the ClinVar database is open to all academic users, users seeking information about a personal medical or genetic condition are urged to consult with a qualified physician for diagnosis and for answers to personal questions. These tracks show the genomic positions of variants in the ClinVar database. ClinVar is a free, public archive of reports of the relationships among human variations and phenotypes, with supporting evidence. Because the ClinVar type no longer captures this information, any variation equal to or larger than 50 bp is now considered a CNV. The ClinVar Interpretations track displays the genomic positions of individual variant submissions and interpretations of the clinical significance and their relationship to disease in the ClinVar database. Variants may be right-aligned or may contain additional context, e.
Clinvar
Genome Medicine volume 15 , Article number: 51 Cite this article. Metrics details. Curated databases of genetic variants assist clinicians and researchers in interpreting genetic variation. Yet, these databases contain some misclassified variants. It is unclear whether variant misclassification is abating as these databases rapidly grow and implement new guidelines. Using archives of ClinVar and HGMD, we investigated how variant misclassification has changed over 6 years, across different ancestry groups. We considered inborn errors of metabolism IEMs screened in newborns as a model system because these disorders are often highly penetrant with neonatal phenotypes. We used samples from the Genomes Project 1KGP to identify individuals with genotypes that were classified by the databases as pathogenic. We observed that African ancestry individuals have a significantly increased chance of being incorrectly indicated to be affected by a screened IEM when HGMD variants are used. However, this bias affecting genomes of African ancestry was no longer significant once common variants were removed in accordance with recent variant classification guidelines. Considering misclassified variants that have since been reclassified reveals our increasing understanding of rare genetic variation. We found that variant classification guidelines and allele frequency databases comprising genetically diverse samples are important factors in reclassification. We also discovered that ClinVar variants common in European and South Asian individuals were more likely to be reclassified to a lower confidence category, perhaps due to an increased chance of these variants being classified by multiple submitters.
Clinical use clinvar current polygenic risk scores may exacerbate health disparities.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. ClinVar accessions submissions reporting human variation, interpretations of the relationship of that variation to human health and the evidence supporting each interpretation. The database is tightly coupled with dbSNP and dbVar, which maintain information about the location of variation on human assemblies. Each ClinVar record represents the submitter, the variation and the phenotype, i. The submitter can update the submission at any time, in which case a new version is assigned.
The content on this website is based on ClinVar database version July 14, Simple ClinVar was developed to provide gene- and disease-wise summary statistic based on all available genetic variants from ClinVar. How many missense variants are associated to heart disease? What are the top 10 genes mutated in Alzheimer? Does CDKL5 have pathogenic mutations? If so, where? Simple ClinVar is able to answer these questions and more, in a matter of seconds. For detailed information about Simple ClinVar please refer to the original publication:.
Clinvar
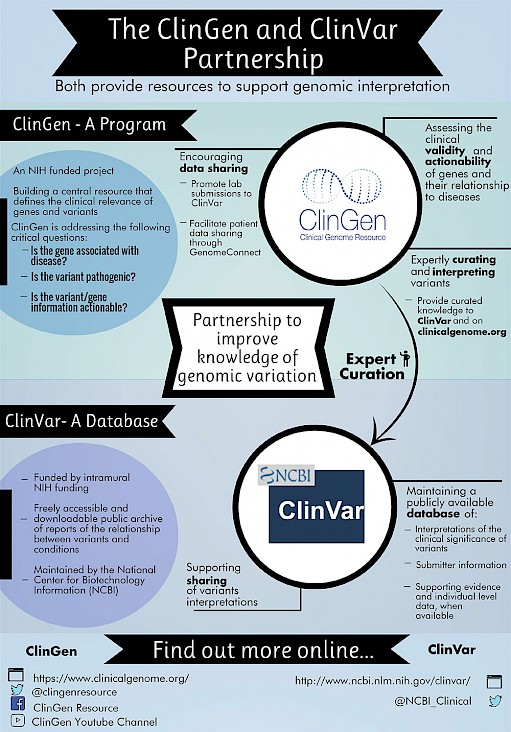
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. ClinVar partners with ClinGen to advance knowledge connecting human variation to human health. Although both support centralization of information to improve access, there are some differences worth noting. This page summarizes functions specific to ClinGen, with links to more information on ClinGen's web site.
Caravan vintage for sale
Metrics details. Using archives of ClinVar and HGMD, we investigated how variant misclassification has changed over 6 years, across different ancestry groups. Clinical Significance Loading An integrated map of genetic variation from 1, human genomes. ClinVar reports multiple types of attributes for each variant. Additional file 2: Table S2. Updated BA1 guidelines to classify common variants as benign remove lingering ancestry-specific false-positive variants Due to founder mutations, individual IEM variants are often enriched in a single ancestry. Newborns in most developed countries are screened for IEMs using blood metabolites. For variants with multiple classifications separated by commas, if exactly one of the classifications was in the above list of categories, the variant was assigned to that category e. Supplementary Information. Updates A submitter can provide an update at any time. Mol Case Stud. A variant-month is a measure of both the number of variants and how long they have been in ClinVar. Show Table. Why rare diseases are an important medical and social issue.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
ClinVar is a submission-driven database that holds both primary submissions and expert-curated submissions. This likely reflects the historical lack of African ancestry samples in large sequencing projects [ 68 , 69 ]. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in , humans. Open in a separate window. View all files. Sharo, A. Please note that esearch [e. F Rate of reclassification of variants shown in E when normalized by historical ancestry composition of variants in ClinVar. Numbers in parentheses provide variant counts of initial and final classifications for each category. If there are SCV records for the same variation and phenotype as the reviewed record, the interpretation on the reviewed record takes precedence over the interpretations from individual submitters. Assessment of the ExAC data set for the presence of individuals with pathogenic genotypes implicated in severe Mendelian pediatric disorders. It serves as the primary site for deposition and retrieval of variant data and annotations from individual submitters. In our analysis of 1KGP-indicated affected individuals, ClinVar submissions were removed from consideration if the submitted condition was not a screened IEM e. Genomic analysis of historical cases with positive newborn screens for short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency shows that a validated second-tier biochemical test can replace future sequencing. After visualizing these reclassifications with Sankey plots, we observed that in many reclassification paths, European variants were not the largest group Fig.

It agree, this magnificent idea is necessary just by the way
I recommend to you to visit a site on which there are many articles on a theme interesting you.